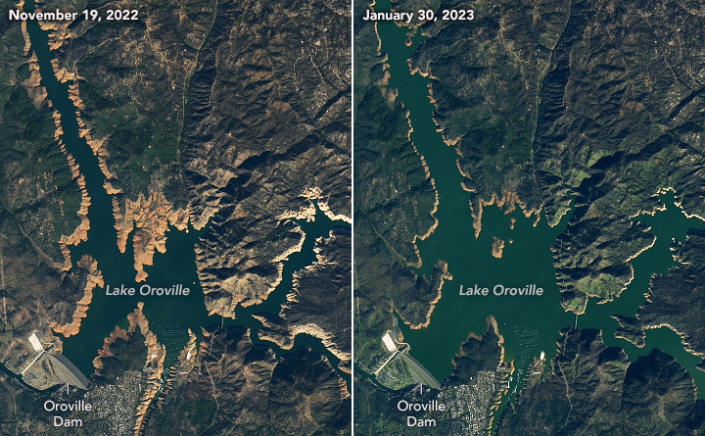
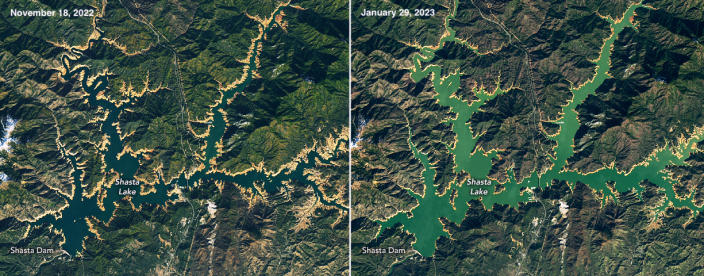
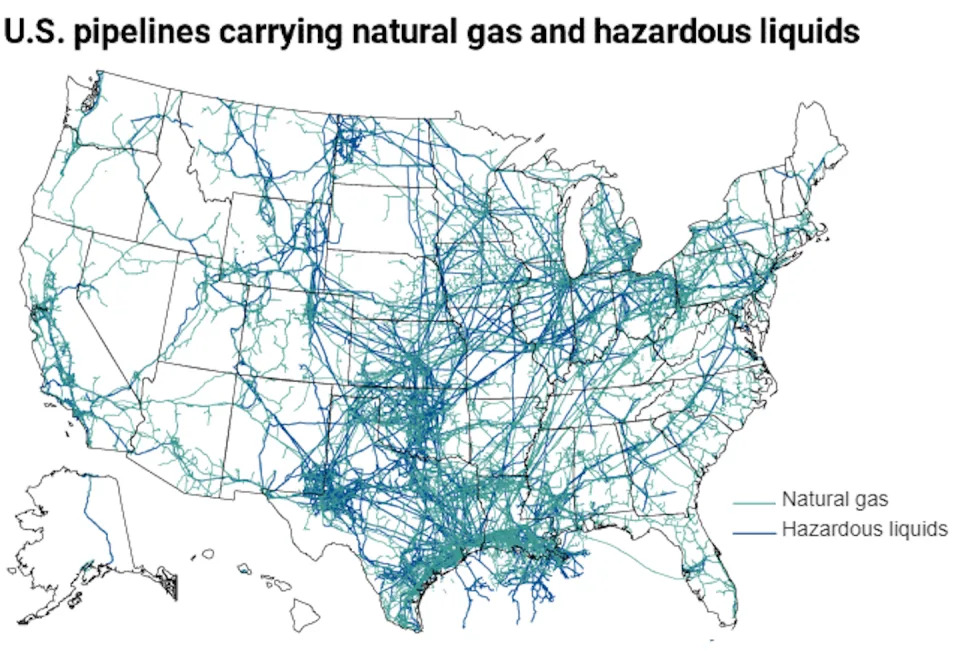
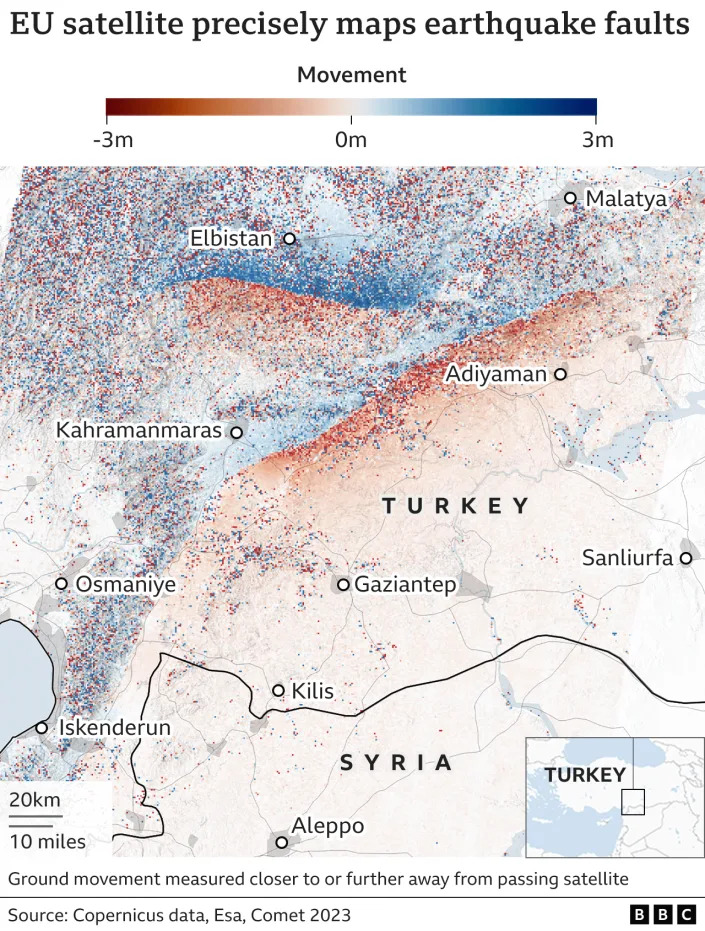
The Conversation
How dangerous was the Ohio chemical train derailment? An environmental engineer assesses the long-term risks
Andrew J. Whelton, Professor of Civil, Environmental & Ecological Engineering, Director of the Healthy Plumbing Consortium and Center for Plumbing Safety, Purdue University – February 15, 2023
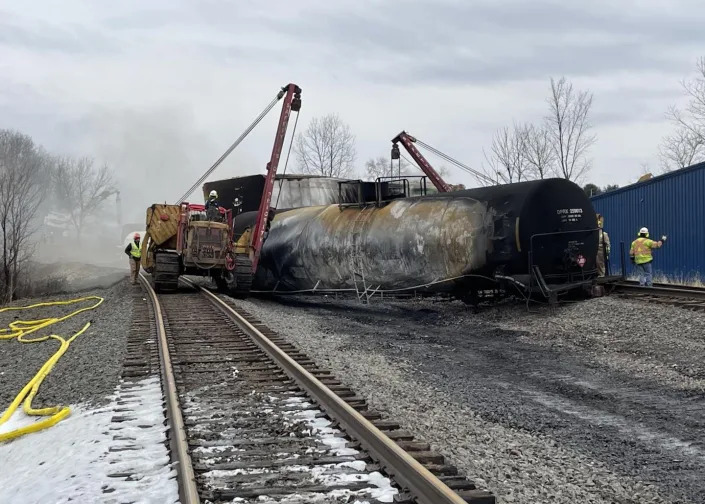

Headaches and lingering chemical smells from a fiery train derailment in East Palestine, Ohio, have left residents worried about their air and water – and misinformation on social media hasn’t helped.
State officials offered more details of the cleanup process and a timeline of the environmental disaster during a news conference on Feb. 14, 2023. Nearly a dozen cars carrying chemicals, including vinyl chloride, a carcinogen, derailed on the evening of Feb. 3, and fire from the site sent up acrid black smoke. Officials said they had tested over 400 nearby homes for contamination and were tracking a plume of spilled chemicals that had killed 3,500 fish in streams and reached the Ohio River.
However, the slow release of information after the derailment has left many questions unanswered about the risks and longer-term impact. We put five questions about the chemical releases to Andrew Whelton, an environmental engineer who investigates chemical risks during disasters.
Let’s start with what was in the train cars. What are the most concerning chemicals for human health and the environment long term, and what’s known so far about the impact?
The main concerns now are the contamination of homes, soil and water, primarily from volatile organic compounds and semivolatile organic compounds, known as VOCs and SVOCs.
The train had nearly a dozen cars with vinyl chloride and other materials, such as ethylhexyl acrylate and butyl acrylate. These chemicals have varying levels of toxicity and different fates in soil and groundwater. Officials have detected some of those chemicals in the nearby waterway and particulate matter in the air from the fire. But so far, the fate of many of the chemicals is not known. A variety of other materials were also released, but discussion about those chemicals has been limited.
State officials disclosed that a plume of contamination released into the nearby creek had made its way into the Ohio River. Other cities get their drinking water from the river, and were warned about the risk. The farther this plume moves downstream, the less concentrated the chemical will be in water, posing less of a risk.
Long term, the greatest risk is closest to the derailment location. And again, there’s limited information about what chemicals are present – or were created through chemical reactions during the fire.
It isn’t clear yet how much went into storm drains, was flushed down the streams or may have settled to the bottom of waterways.
There was also a lot of combusted particulate matter. The black smoke is a clear indication. It’s unclear how much was diluted in the air or fell to the ground.
How long can these chemicals linger in soil and water, and what’s their potential long-term risk to humans and wildlife?
The heavier the chemical, often the slower it degrades and the more likely it is to stick to soil. These compounds can remain for years if left unaddressed.
After the Kalamazoo River oil pipeline break in Michigan in 2010, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency excavated a tributary where the oil settled. We’ve also seen from oil spills on the coasts of Alaska and Alabama that oil chemicals can find their way into soil if it isn’t remediated.
The long-term impact in Ohio will depend in part on how fast – and thoroughly – cleanup occurs.
If the heavily contaminated soils and liquids are excavated and removed, the long-term impacts can be reduced. But the longer removal takes, the farther the contamination can spread. It’s in everyone’s best interest to clean this up as soon as possible and before the region gets rain.
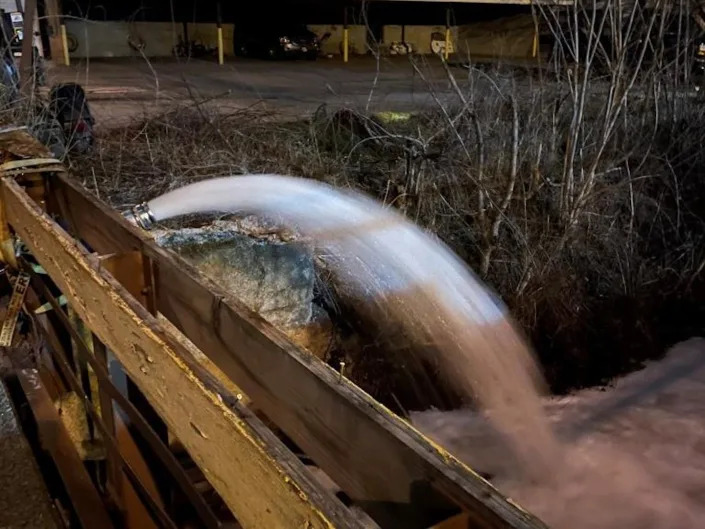

Booms in a nearby stream have been deployed to capture chemicals. Air-stripping devices have been deployed to remove chemicals from the waterways. Air stripping causes the light chemicals to leave the water and enter air. This is a common treatment technique and was used after an 2015 oil spill in the Yellowstone River near Glendive, Montana.
At the derailment site in Ohio, workers are already removing contaminated soil as deep as 7 feet (about 2 meters) near where the rail cars burned.
Some of the train cars were intentionally drained and the chemicals set on fire to eliminate them. That fire had thick black smoke. What does that tell you about the chemicals and longer-term risks?
Incineration is one way we dispose of hazardous chemicals, but incomplete chemical destruction creates a host of byproducts. Chemicals can be destroyed when heated to extremely high temperatures so they burn thoroughly.
The black smoke plume you saw on TV was incomplete combustion. A number of other chemicals were created. Officials don’t necessarily know what these were or where they went until they test for them.
We know ash can pose health risks, which is why we test inside homes after wildfires where structures burn. This is one reason the state’s health director told residents with private wells near and downwind of the derailment to use bottled water until they can have their wells tested.
The EPA has been screening homes near the derailment for indoor air-quality concerns. How do these chemicals get into homes and what happens to them in enclosed spaces?
Homes are not airtight, and sometimes dust and other materials get in. It might be through an open door or a window sill. Sometimes people track it in.
So far, the U.S. EPA has reported no evidence of high levels of vinyl chloride or hydrogen chloride in the 400 or so homes tested. But full transparency has been lacking. Just because an agency is doing testing doesn’t mean it is testing for what it needs to test for.
Media reports talk about four or five chemicals, but the manifest from Norfolk Southern also listed a bunch of other materials in tanks that burned. All those materials create potentially hundreds to thousands of VOCs and SVOCs.
Are government officials testing for everything they should?
People in the community have reported headaches, which can be caused by VOCs and other chemicals. They’re understandably concerned.
Ohio and federal officials need to better communicate what they’re doing, why, and what they plan to do. It’s unclear what questions they are trying to answer. For a disaster this serious, little testing information has been shared.
In the absence of this transparency, misinformation is filling that void. From a homeowner’s perspective, it’s hard to understand the true risk if the data is not shared.