The New York Times
Trump Wants to Prosecute Biden. He Also Thinks Presidents Deserve Immunity.
Alan Feuer and Maggie Haberman – April 30, 2024

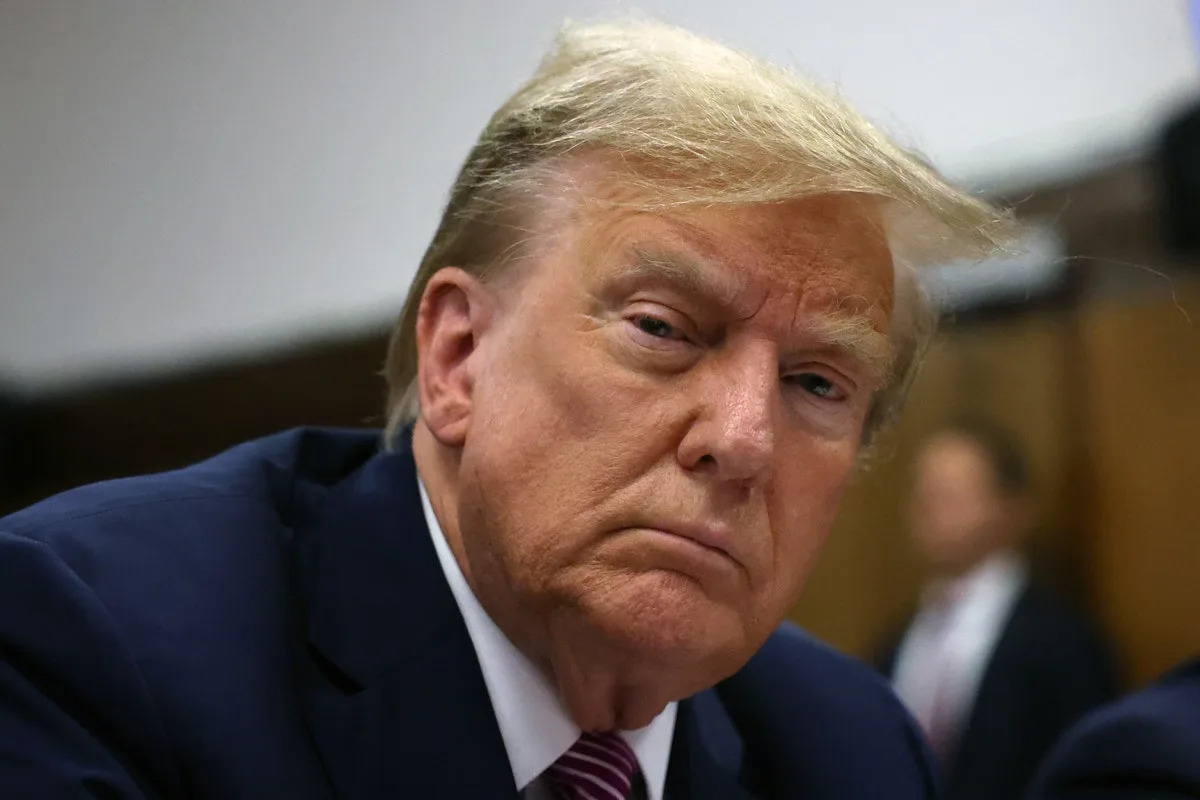
When a lawyer for former President Donald Trump argued before the Supreme Court last week that his client should be immune from charges of plotting to subvert the last election, he asked the justices to picture a world in which former presidents were ceaselessly pursued in the courts by their successors.
“Could President Biden someday be charged with unlawfully inducing immigrants to enter the country illegally for his border policies?” the lawyer, D. John Sauer, asked.
What Sauer did not mention was that Trump has done as much as anyone to escalate the prospect of threatening political rivals with prosecution. In 2016, his supporters greeted mentions of Hillary Clinton with chants of, “Lock her up.” In his current campaign, Trump has explicitly warned of his intent to use the legal system as a weapon of political retribution, with frequent declarations that he could go after President Joe Biden and his family.
In effect, Trump has asked the Supreme Court to enforce a norm — that in the United States, public officials do not engage in tit-for-tat political prosecutions — that he has for years threatened to shatter. In promising to sic his Justice Department on Biden, Trump has laid the grounds for the very conditions that he was asking the justices to guard against by granting him immunity.
Trump’s perspective is that it is Biden who has politicized justice by pursuing him on multiple fronts as they face each other on the campaign trail. In making that argument, however, Trump has sought to evade the reality that no former president has been faced with as many allegations, or as much evidence, of wrongdoing as he has.
The two federal cases against Trump were brought by a special counsel operating largely independently of the Justice Department, while the two other criminal cases against him were brought by local district attorneys in New York and Georgia.
Paradoxically, should the Supreme Court decide that presidents do enjoy some degree of immunity for their official actions while in office, the ruling would deprive Trump of one of the major themes that he and his allies have promoted throughout the current campaign: that Biden needs to be held to account by the criminal justice system, despite the lack of compelling evidence that he has violated any laws.
And should Trump win in November, he would find it far more difficult, if not impossible, to bring a case against Biden for any actions Biden took in office.
Last spring, Trump vowed that if he was elected again, he would appoint a special counsel to “go after” Biden and his family. And as recently as two weeks ago, he posted a not-so-veiled threat on social media, saying that if the Supreme Court rejected his claims of presidential immunity, it would also “take away” Biden’s immunity.
Over the weekend, Eric Trump, one of Trump’s sons, weighed in about a future prosecution of Biden. Appearing on Fox News, he said that if the court denied immunity to his father, it would mean that “they” — he did not say exactly who he meant — would be able to pursue Biden for things like having depleted the national petroleum reserve.
“The floodgates are going to open,” Eric Trump said. “And I guarantee you Joe Biden will not have one foot outside of the White House doors before they start going after him legally.”
Such remarks have become a staple of Donald Trump’s presidential campaign, as he has focused his political message on the four criminal cases he is facing.
History has already shown that the former president and his allies have been willing to use the judicial system against their perceived adversaries.
Trump’s Justice Department, under the control of former Attorney General William Barr, appointed a special counsel, John Durham, to investigate the investigators who launched the inquiry into connections between Russia and Trump’s 2016 presidential campaign.
Trump also repeatedly encouraged inquiries into his political critics, including Clinton; James Comey, whom he fired as the FBI director; and John Kerry, the former senator and secretary of state under President Barack Obama. (None of them were prosecuted.)
As president, Trump wanted a number of his perceived political enemies, including Comey, to be investigated by the IRS, according to one of his White House chiefs of staff.
For all of Trump’s promises to bring some sort of criminal investigation against Biden, however, the vows have come as actual evidence of offenses by the president has been hard to find.
After more than a year of investigation, House Republicans have seemed to retreat from their attempts to bring impeachment charges against Biden. A separate impeachment proceeding against Alejandro Mayorkas, Biden’s homeland security secretary, was quickly cast aside when it reached the Senate.
In February, special counsel Robert Hur said there was insufficient evidence to charge Biden with illegally holding on to classified documents after he served as vice president.
Given the long acceptance of the American legal principle that no one is above the law, Trump’s immunity claim seemed like a long shot when his lawyers took it before the Supreme Court.
Still, some of the court’s conservative justices appeared last week to accept Trump’s underlying argument that in a polarized political environment, all presidents could be charged with something when they got out of office if he did not receive the protections of immunity.
“It’s going to cycle back and be used against the current president or the next president,” Justice Brett Kavanaugh said, “and the next president and the next president after that.”
It is impossible to know just how much protection, if any, the justices will ultimately grant Trump in the election interference case. While none of them appeared to embrace his most extreme idea — that he could not be prosecuted at all unless first convicted at an impeachment trial — several seemed to agree that he might enjoy a limited form of immunity that would shield him from being charged for official actions central to his job.
As for Biden, all of the grounds for bringing a case against him that have been floated by Trump, his allies or his lawyers have had little basis in the law. Those grounds would be even harder to support if the Supreme Court were inclined to limit prosecutions based on a former president’s core official acts.
Eric Trump’s suggestion of going after Biden over his handling of the petroleum reserve, for instance, would seem to fall squarely within the realm of a president’s official duties. So would Sauer’s idea of prosecuting Biden for his border policy.
Even though some form of executive immunity could one day protect Biden against an attack from prosecutors under Trump, Michael Dreeben, a lawyer who argued for the Justice Department, told the court that it was neither necessary or desirable.
The criminal justice system, Dreeben said, already had “layered safeguards” in place to ensure against what he called “a runaway train” of rogue indictments.
What was far more worrying, Drebeen argued, was creating a form of immunity that could allow a president to commit crimes with impunity.
“The framers knew too well the dangers of a king who could do no wrong,” he said. “They therefore devised a system to check abuses of power, especially the use of official power for private gain.”