Miami Herald
Gov. DeSantis is banking on Americans hating immigrants more than high insurance rates | Opinion
Fabiola Santiago – May 12, 2023
He’s got your back on the hate, red Floridians.
For starters, millions of your tax dollars have been designated by Gov. Ron DeSantis and the Legislature — no, not to subsidize our skyrocketing home insurance — but to ship planeloads of new immigrants to blue states.
The governor will fish them from the sea, if he has to, for publicity stunts.
His presidential aspirations need shocker headlines — and the oxygen in his $117 billion big government budget only left room for catering to your irrational immigrant-loathing and to fighting Disney World in courts over one opinion contrary to his.
Immigrant-hunting will be as expensive as the well-paid lawyers DeSantis is employing to uphold civil rights violations.
By signing into law a sweeping anti-immigrant bill, DeSantis has built his own wall around the state’s sea and land borders, hoping to outdo Donald Trump’s U.S.-Mexico effort, wimpy and inefficient by comparison.
The Republican governor and his sycophant Legislature figured out that all they had to do was terrorize people with the ruthless contents of SB 1718 — and asylum-seekers wouldn’t confuse the Sunshine State for a sanctuary.
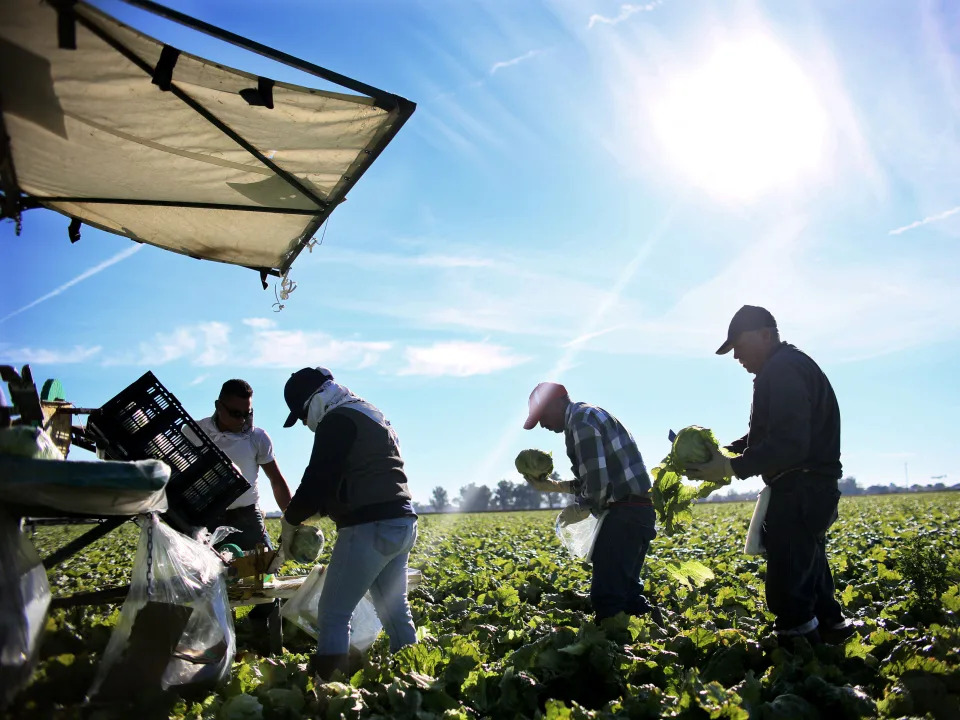
It’s already working so well that immigrant construction workers in South Florida weren’t showing up to work this week for fear that there would be a round-up and they’d be deported, CBS News Miami reported.
Red mandates
DeSantis calls his mandates “the strongest anti-illegal immigration law in the country to combat Biden’s border crisis.”
Ironically, he’s promoting the message in an explanatory document set in bold red and black lettering — the colors of Fidel Castro’s 26th of July Movement in Cuba and the Sandinistas’ National Liberation Front in Nicaragua, regimes from which immigrants are fleeing.
The new Florida immigration law, effective July 1, allows random audits of employers suspected of hiring unauthorized immigrant workers — opening the door to ethnic and racial profiling.
All those Hispanic business owners in Miami-Dade and other immigrant-populated communities who voted for DeSantis are being richly rewarded. (There’s a more appropriate verb that starts with an “s,” but I’m not allowed to use it). I don’t feel sorry for these voters. But I do for hard-working undocumented immigrants who aren’t hurting anyone and the families who love them.
The medical field — those providing care and their patients — will also be adversely affected.
If an immigrant without legal status has a medical emergency — a life-threatening illness, is having a baby or had a car accident, makes no difference — the law now requires that hospitals collect data about patients’ immigration status and document the money spent on providing them healthcare.
In addition, no Florida government entity is allowed to issue to immigrants an identification card of any kind, even if they have passports or birth certificates. Can’t get one without proof of legal entry.
People driving without a license is just what we need in Florida. And, nope, relatives can’t drive the undocumented, either, and stay within the law themselves. Drivers can be charged with a third-degree felony for knowingly giving an undocumented migrant a lift to church, school or work.
Do so, and risk being charged as a human smuggler.
In Miami, this means all the Cubans and Venezuelans who love Trump and DeSantis so much — and are housing, hosting, transporting or providing medical care for anyone without the right documentation — now have enforced restrictions to keep in mind.
If they operate as they have until now, on the fly, they become law-breakers.
Then, there’s the tightening of E-Verify, which makes it more difficult than ever for workplaces to hire immigrants.
A federal program for employers to confirm a person’s immigration status, operating since 1996, it became voluntary when President Bill Clinton signed it into law under the Illegal Immigrant Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act. Later required, the program was expanded and made easier to use under President Barack Obama.
Not good enough for DeSantis, who says his state will strictly enforce E-Verify: Employers with 25 or more workers have to put through the system everyone’s immigration status — or face a $1,000 per day fine if an employee is found to be in the country illegally.
All companies, no matter whether they maintain your lawn, paint the walls or put on a new roof, have to comply. So the able-bodied, quick-learning, eager-to-work rafter who just got off the boat can’t work at your house.
No, Florida is no longer a place where immigrants can rebuild — in peace — lives lost to dictatorship, poverty, and violence, while in the process, contributing desperately needed labor to the United States economy.
Without a care for the state’s history (maybe he is a Midwesterner, as he tries to pass off himself in his political pamphlet-styled memoir) DeSantis — with the help of shameless legislators who are the descendants of exiles and other immigrants — has shut the door.
Why the persecution?
The governor needs your red vote badly to win the Republican presidential primary — and he’s sure that crushing immigrants is the key to voters’ hearts. So much so that he forgot all about the damage those pesky hurricanes and rising seas bring and the ensuing reconstruction.
But no worries about a state dependent on agriculture, tourism and construction, left without immigrant labor.
Write with a smile the big check to the insurance company that, after decades of paying, will tell you when you most need them — as is happening now to the insured in southwest Florida repairing homes destroyed by Hurricane Ian: The fancy door is a decoration and isn’t covered.
Write with a spring in your step the big check to the construction company charging you more because the owner can’t hire cheaper labor.
Your man in Tallahassee has delivered!
Now you can peel your eyes away from the white-world-is-ending Fox News reports from the southern border.
They really are bad for your health. The surge in blood pressure can provoke a stroke — and there won’t be a cheap, undocumented immigrant your family can hire to change your diaper.
This is the new world DeSantis and the Florida GOP have created, one conceived in hatred of The Other who, more often than not, was making our lives better.