New Republic
Trump’s Russian Laundromat
How to use Trump Tower and other luxury high-rises to clean dirty money, run an international crime syndicate, and propel a failed real estate developer into the White House.
By Craig Unger July 13, 2017
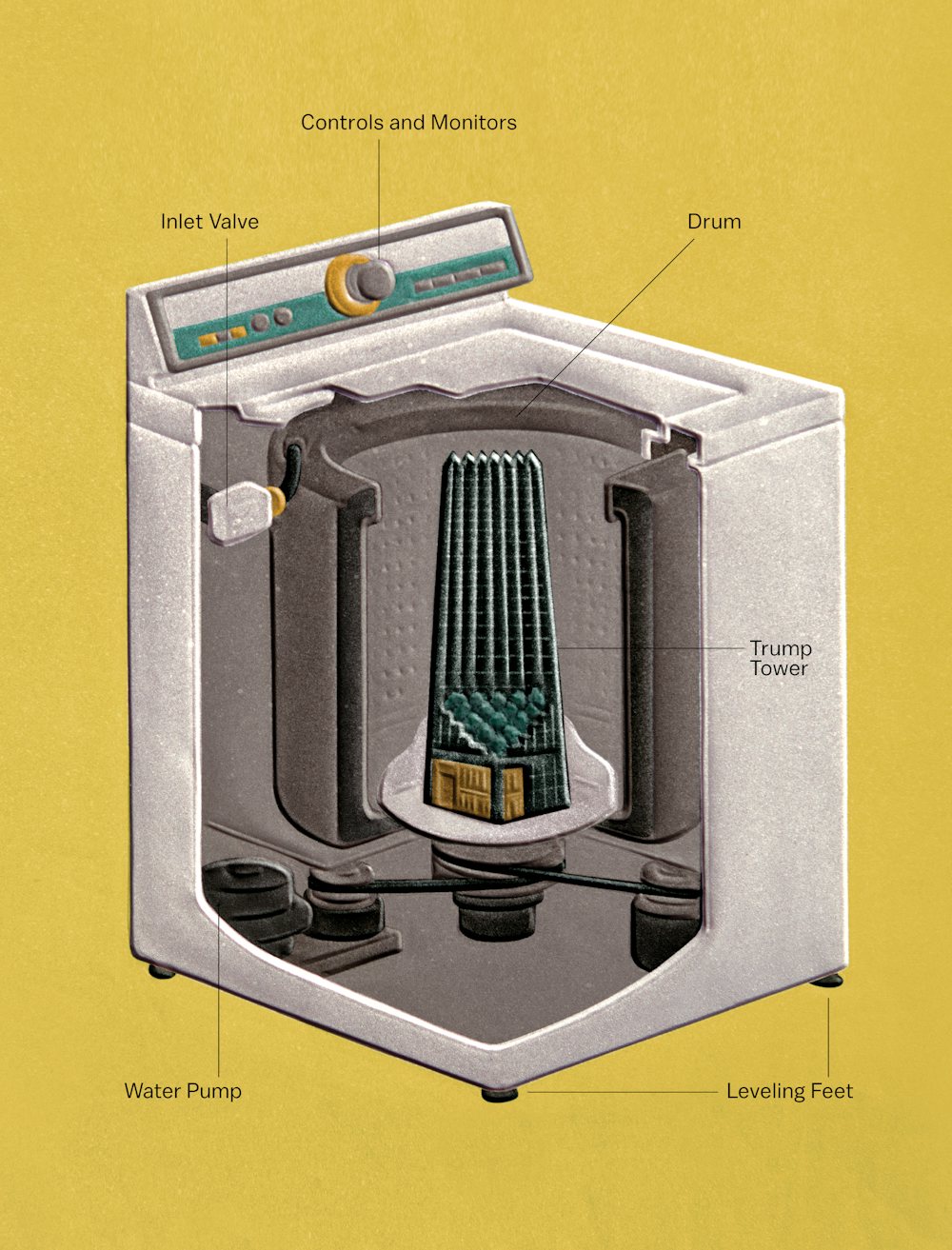
Illustration by Alex Nabaum
In 1984, a Russian émigré named David Bogatin went shopping for apartments in New York City. The 38-year-old had arrived in America seven years before, with just $3 in his pocket. But for a former pilot in the Soviet Army—his specialty had been shooting down Americans over North Vietnam—he had clearly done quite well for himself. Bogatin wasn’t hunting for a place in Brighton Beach, the Brooklyn enclave known as “Little Odessa” for its large population of immigrants from the Soviet Union. Instead, he was fixated on the glitziest apartment building on Fifth Avenue, a gaudy, 58-story edifice with gold-plated fixtures and a pink-marble atrium: Trump Tower.
A monument to celebrity and conspicuous consumption, the tower was home to the likes of Johnny Carson, Steven Spielberg, and Sophia Loren. Its brash, 38-year-old developer was something of a tabloid celebrity himself. Donald Trump was just coming into his own as a serious player in Manhattan real estate, and Trump Tower was the crown jewel of his growing empire. From the day it opened, the building was a hit—all but a few dozen of its 263 units had sold in the first few months. But Bogatin wasn’t deterred by the limited availability or the sky-high prices. The Russian plunked down $6 million to buy not one or two, but five luxury condos. The big check apparently caught the attention of the owner. According to Wayne Barrett, who investigated the deal for the Village Voice, Trump personally attended the closing, along with Bogatin.
If the transaction seemed suspicious—multiple apartments for a single buyer who appeared to have no legitimate way to put his hands on that much money—there may have been a reason. At the time, Russian mobsters were beginning to invest in high-end real estate, which offered an ideal vehicle to launder money from their criminal enterprises. “During the ’80s and ’90s, we in the U.S. government repeatedly saw a pattern by which criminals would use condos and high-rises to launder money,” says Jonathan Winer, a deputy assistant secretary of state for international law enforcement in the Clinton administration. “It didn’t matter that you paid too much, because the real estate values would rise, and it was a way of turning dirty money into clean money. It was done very systematically, and it explained why there are so many high-rises where the units were sold but no one is living in them.” When Trump Tower was built, as David Cay Johnston reports in The Making of Donald Trump, it was only the second high-rise in New York that accepted anonymous buyers.
In 1987, just three years after he attended the closing with Trump, Bogatin pleaded guilty to taking part in a massive gasoline-bootlegging scheme with Russian mobsters. After he fled the country, the government seized his five condos at Trump Tower, saying that he had purchased them to “launder money, to shelter and hide assets.” A Senate investigation into organized crime later revealed that Bogatin was a leading figure in the Russian mob in New York. His family ties, in fact, led straight to the top: His brother ran a $150 million stock scam with none other than Semion Mogilevich, whom the FBI considers the “boss of bosses” of the Russian mafia. At the time, Mogilevich—feared even by his fellow gangsters as “the most powerful mobster in the world”—was expanding his multibillion-dollar international criminal syndicate into America.
Since Trump’s election as president, his ties to Russia have become the focus of intense scrutiny, most of which has centered on whether his inner circle colluded with Russia to subvert the U.S. election. A growing chorus in Congress is also asking pointed questions about how the president built his business empire. Rep. Adam Schiff, the ranking Democrat on the House Intelligence Committee, has called for a deeper inquiry into “Russian investment in Trump’s businesses and properties.”
The very nature of Trump’s businesses—all of which are privately held, with few reporting requirements—makes it difficult to root out the truth about his financial deals. And the world of Russian oligarchs and organized crime, by design, is shadowy and labyrinthine. For the past three decades, state and federal investigators, as well as some of America’s best investigative journalists, have sifted through mountains of real estate records, tax filings, civil lawsuits, criminal cases, and FBI and Interpol reports, unearthing ties between Trump and Russian mobsters like Mogilevich. To date, no one has documented that Trump was even aware of any suspicious entanglements in his far-flung businesses, let alone that he was directly compromised by the Russian mafia or the corrupt oligarchs who are closely allied with the Kremlin. So far, when it comes to Trump’s ties to Russia, there is no smoking gun.
But even without an investigation by Congress or a special prosecutor, there is much we already know about the president’s debt to Russia. A review of the public record reveals a clear and disturbing pattern: Trump owes much of his business success, and by extension his presidency, to a flow of highly suspicious money from Russia. Over the past three decades, at least 13 people with known or alleged links to Russian mobsters or oligarchs have owned, lived in, and even run criminal activities out of Trump Tower and other Trump properties. Many used his apartments and casinos to launder untold millions in dirty money. Some ran a worldwide high-stakes gambling ring out of Trump Tower—in a unit directly below one owned by Trump. Others provided Trump with lucrative branding deals that required no investment on his part. Taken together, the flow of money from Russia provided Trump with a crucial infusion of financing that helped rescue his empire from ruin, burnish his image, and launch his career in television and politics. “They saved his bacon,” says Kenneth McCallion, a former assistant U.S. attorney in the Reagan administration who investigated ties between organized crime and Trump’s developments in the 1980s.
It’s entirely possible that Trump was never more than a convenient patsy for Russian oligarchs and mobsters, with his casinos and condos providing easy pass-throughs for their illicit riches. At the very least, with his constant need for new infusions of cash and his well-documented troubles with creditors, Trump made an easy “mark” for anyone looking to launder money. But whatever his knowledge about the source of his wealth, the public record makes clear that Trump built his business empire in no small part with a lot of dirty money from a lot of dirty Russians—including the dirtiest and most feared of them all.
Trump made his first trip to Russia in 1987, only a few years before the collapse of the Soviet Union. Invited by Soviet Ambassador Yuri Dubinin, Trump was flown to Moscow and Leningrad—all expenses paid—to talk business with high-ups in the Soviet command. In The Art of the Deal, Trump recounted the lunch meeting with Dubinin that led to the trip. “One thing led to another,” he wrote, “and now I’m talking about building a large luxury hotel, across the street from the Kremlin, in partnership with the Soviet government.”
Over the years, Trump and his sons would try and fail five times to build a new Trump Tower in Moscow. But for Trump, what mattered most were the lucrative connections he had begun to make with the Kremlin—and with the wealthy Russians who would buy so many of his properties in the years to come. “Russians make up a pretty disproportionate cross section of a lot of our assets,” Donald Trump Jr. boasted at a real estate conference in 2008. “We see a lot of money pouring in from Russia.”
The money, illicit and otherwise, began to rain in earnest after the Soviet Union fell in 1991. President Boris Yeltsin’s shift to a market economy was so abrupt that cash-rich gangsters and corrupt government officials were able to privatize and loot state-held assets in oil, coal, minerals, and banking. Yeltsin himself, in fact, would later describe Russia as “the biggest mafia state in the world.” After Vladimir Putin succeeded Yeltsin as president, Russian intelligence effectively joined forces with the country’s mobsters and oligarchs, allowing them to operate freely as long as they strengthen Putin’s power and serve his personal financial interests. According to James Henry, a former chief economist at McKinsey & Company who consulted on the Panama Papers, some $1.3 trillion in illicit capital has poured out of Russia since the 1990s.
At the top of the sprawling criminal enterprise was Semion Mogilevich. Beginning in the early 1980s, according to the FBI, the short, squat Ukrainian was the key money-laundering contact for the Solntsevskaya Bratva, or Brotherhood, one of the richest criminal syndicates in the world. Before long, he was running a multibillion-dollar worldwide racket of his own. Mogilevich wasn’t feared because he was the most violent gangster, but because he was reputedly the smartest. The FBI has credited the “brainy don,” who holds a degree in economics from Lviv University, with a staggering range of crimes. He ran drug trafficking and prostitution rings on an international scale; in one characteristic deal, he bought a bankrupt airline to ship heroin from Southeast Asia into Europe. He used a jewelry business in Moscow and Budapest as a front for art that Russian gangsters stole from museums, churches, and synagogues all over Europe. He has also been accused of selling some $20 million in stolen weapons, including ground-to-air missiles and armored troop carriers, to Iran. “He uses this wealth and power to not only further his criminal enterprises,” the FBI says, “but to influence governments and their economies.”
In Russia, Mogilevich’s influence reportedly reaches all the way to the top. In 2005, Alexander Litvinenko, a Russian intelligence agent who defected to London, recorded an interview with investigators detailing his inside knowledge of the Kremlin’s ties to organized crime. “Mogilevich,” he said in broken English, “have good relationship with Putin since 1994 or 1993.” A year later Litvinenko was dead, apparently poisoned by agents of the Kremlin.
Mogilevich’s greatest talent, the one that places him at the top of the Russian mob, is finding creative ways to cleanse dirty cash. According to the FBI, he has laundered money through more than 100 front companies around the world, and held bank accounts in at least 27 countries. And in 1991, he made a move that led directly to Trump Tower. That year, the FBI says, Mogilevich paid a Russian judge to spring a fellow mob boss, Vyachelsav Kirillovich Ivankov, from a Siberian gulag. If Mogilevich was the brains, Ivankov was the enforcer—a vor v zakone, or “made man,” infamous for torturing his victims and boasting about the murders he had arranged. Sprung by Mogilevich, Ivankov made the most of his freedom. In 1992, a year after he was released from prison, he headed to New York on an illegal business visa and proceeded to set up shop in Brighton Beach.
In Red Mafiya, his book about the rise of the Russian mob in America, investigative reporter Robert I. Friedman documented how Ivankov organized a lurid and violent underworld of tattooed gangsters. When Ivankov touched down at JFK, Friedman reported, he was met by a fellow vor, who handed him a suitcase with $1.5 million in cash. Over the next three years, Ivankov oversaw the mob’s growth from a local extortion racket to a multibillion-dollar criminal enterprise. According to the FBI, he recruited two “combat brigades” of Special Forces veterans from the Soviet war in Afghanistan to run the mafia’s protection racket and kill his enemies.
Like Mogilevich, Ivankov had a lot of dirty money he needed to clean up. He bought a Rolls-Royce dealership that was used, according to The New York Times, “as a front to launder criminal proceeds.” The FBI concluded that one of Ivankov’s partners in the operation was Felix Komarov, an upscale art dealer who lived in Trump Plaza on Third Avenue. Komarov, who was not charged in the case, called the allegations baseless. He acknowledged that he had frequent phone conversations with Ivankov, but insisted the exchanges were innocent. “I had no reason not to call him,” Komarov told a reporter.
Trump Taj Mahal paid the largest fine ever levied against a casino for having “willfully violated” anti-money-laundering rules.
The feds wanted to arrest Ivankov, but he kept vanishing. “He was like a ghost to the FBI,” one agent recalls. Agents spotted him meeting with other Russian crime figures in Miami, Los Angeles, Boston, and Toronto. They also found he made frequent visits to Trump Taj Mahal in Atlantic City, which mobsters routinely used to launder huge sums of money. In 2015, the Taj Mahal was fined $10 million—the highest penalty ever levied by the feds against a casino—and admitted to having “willfully violated” anti-money-laundering regulations for years.
The FBI also struggled to figure out where Ivankov lived. “We were looking around, looking around, looking around,” James Moody, chief of the bureau’s organized crime section, told Friedman. “We had to go out and really beat the bushes. And then we found out that he was living in a luxury condo in Trump Tower.”
There is no evidence that Trump knew Ivankov personally, even if they were neighbors. But the fact that a top Russian mafia boss lived and worked in Trump’s own building indicates just how much high-level Russian mobsters came to view the future president’s properties as a home away from home. In 2009, after being extradited to Russia to face murder charges, Ivankov was gunned down in a sniper attack on the streets of Moscow. According to The Moscow Times, his funeral was a media spectacle in Russia, attracting “1,000 people wearing black leather jackets, sunglasses, and gold chains,” along with dozens of giant wreaths from the various brotherhoods.
Throughout the 1990s, untold millions from the former Soviet Union flowed into Trump’s luxury developments and Atlantic City casinos. But all the money wasn’t enough to save Trump from his own failings as a businessman. He owed $4 billion to more than 70 banks, with a mind-boggling $800 million of it personally guaranteed. He spent much of the decade mired in litigation, filing for multiple bankruptcies and scrambling to survive. For most developers, the situation would have spelled financial ruin. But fortunately for Trump, his own economic crisis coincided with one in Russia.
In 1998, Russia defaulted on $40 billion in debt, causing the ruble to plummet and Russian banks to close. The ensuing financial panic sent the country’s oligarchs and mobsters scrambling to find a safe place to put their money. That October, just two months after the Russian economy went into a tailspin, Trump broke ground on his biggest project yet. Rising to 72 stories in midtown Manhattan, Trump World Tower would be the tallest residential building on the planet. Construction got underway in 1999—just as Trump was preparing his first run for the presidency on the Reform Party ticket— and concluded in 2001. As Bloomberg Businessweek reported earlier this year, it wasn’t long before one-third of the units on the tower’s priciest floors had been snatched up—either by individual buyers from the former Soviet Union, or by limited liability companies connected to Russia. “We had big buyers from Russia and Ukraine and Kazakhstan,” sales agent Debra Stotts told Bloomberg.

Among the new tenants was Eduard Nektalov, a diamond dealer from Uzbekistan. Nektalov, who was being investigated by a Treasury Department task force for mob-connected money laundering, bought a condo on the seventy-ninth floor, directly below Trump’s future campaign manager, Kellyanne Conway. A month later he sold his unit for a $500,000 profit. The following year, after rumors circulated that Nektalov was cooperating with federal investigators, he was shot down on Sixth Avenue.
Trump had found his market. After Trump World Tower opened, Sotheby’s International Realty teamed up with a Russian real estate company to make a big sales push for the property in Russia. The “tower full of oligarchs,” as Bloomberg called it, became a model for Trump’s projects going forward. All he needed to do, it seemed, was slap the Trump name on a big building, and high-dollar customers from Russia and the former Soviet republics were guaranteed to come rushing in. Dolly Lenz, a New York real estate broker, told USA Today that she sold some 65 units in Trump World Tower to Russians. “I had contacts in Moscow looking to invest in the United States,” Lenz said. “They all wanted to meet Donald.”
To capitalize on his new business model, Trump struck a deal with a Florida developer to attach his name to six high-rises in Sunny Isles, just outside Miami. Without having to put up a dime of his own money, Trump would receive a cut of the profits. “Russians love the Trump brand,” Gil Dezer, the Sunny Isles developer, told Bloomberg. A local broker told The Washington Post that one-third of the 500 apartments he’d sold went to “Russian-speakers.” So many bought the Trump-branded apartments, in fact, that the area became known as “Little Moscow.”
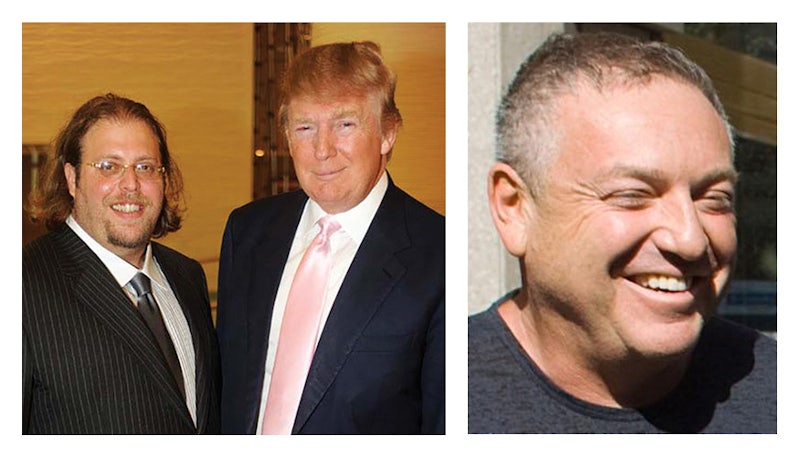
“Russians love the Trump brand,” said developer Gil Dezer, (left, with Trump). One Florida tenant, Anatoly Golubchik (right) was busted in a major money-laundering ring run out of Trump Tower. Billy Farrell/Patrick McMullan/Getty; John Marshall Mantel/ New York Times/Redux
Many of the units were sold by a native of Uzbekistan who had immigrated from the Soviet Union in the 1980s; her business was so brisk that she soon began bringing Russian tour groups to Sunny Isles to view the properties. According to a Reuters investigation in March, at least 63 buyers with Russian addresses or passports spent $98 million on Trump’s properties in south Florida. What’s more, another one-third of the units—more than 700 in all—were bought by shadowy shell companies that concealed the true owners.
Trump promoted and celebrated the properties. His organization continues to advertise the units; in 2011, when they first turned a profit, he attended a ceremonial mortgage-burning in Sunny Isles to toast their success. Last October, an investigation by the Miami Herald found that at least 13 buyers in the Florida complex have been the target of government investigations, either personally or through their companies, including “members of a Russian-American organized crime group.” Two buyers in Sunny Isles, Anatoly Golubchik and Michael Sall, were convicted for taking part in a massive international gambling and money-laundering syndicate that was run out of Trump Tower in New York. The ring, according to the FBI, was operating under the protection of the Russian mafia.
The influx of Russian money did more than save Trump’s business from ruin—it set the stage for the next phase of his career. By 2004, to the outside world, it appeared that Trump was back on top after his failures in Atlantic City. That January, flush with the appearance of success, Trump launched his newly burnished brand into another medium.
“My name’s Donald Trump,” he declared in his opening narration for The Apprentice, “the largest real estate developer in New York. I own buildings all over the place. Model agencies. The Miss Universe pageant. Jetliners, golf courses, casinos, and private resorts like Mar-a-Lago, one of the most spectacular estates anywhere in the world.”
But it wouldn’t be Trump without a better story than that. “It wasn’t always so easy,” he confessed, over images of him cruising around New York in a stretch limo. “About 13 years ago, I was seriously in trouble. I was billions of dollars in debt. But I fought back, and I won. Big league. I used my brain. I used my negotiating skills. And I worked it all out. Now my company’s bigger than it ever was and stronger than it ever was.… I’ve mastered the art of the deal.”
The show, which reportedly paid Trump up to $3 million per episode, instantly revived his career. “The Apprentice turned Trump from a blowhard Richie Rich who had just gone through his most difficult decade into an unlikely symbol of straight talk, an evangelist for the American gospel of success, a decider who insisted on standards in a country that had somehow slipped into handing out trophies for just showing up,” journalists Michael Kranish and Marc Fisher observe in their book Trump Revealed. “Above all, Apprentice sold an image of the host-boss as supremely competent and confident, dispensing his authority and getting immediate results. The analogy to politics was palpable.”
Russians spent at least $98 million on Trump’s properties in Florida—and another third of the units were bought by shadowy shell companies.
But the story of Donald Trump, self-made business genius, left out any mention of the shady Russian investors who had done so much to make his comeback narrative possible. And Trump’s business, despite the hype, was hardly “stronger than it ever was”—his credit was still lousy, and two more of his prized properties in Atlantic City would soon fall into bankruptcy, even as his ratings soared.
To further enhance his brand, Trump used his prime-time perch to unveil another big project. On the 2006 season finale of The Apprentice, as 11 million viewers waited to learn which of the two finalists was going to be fired, Trump prolonged the suspense by cutting to a promotional video for his latest venture. “Located in the center of Manhattan’s chic artist enclave, the Trump International Hotel and Tower in SoHo is the site of my latest development,” he narrated over swooping helicopter footage of lower Manhattan. The new building, he added, would be nothing less than a “$370 million work of art … an awe-inspiring masterpiece.”
Trump SoHo was the brainchild of two development companies—Bayrock Group LLC and the Sapir Organization—run by a pair of wealthy émigrés from the former Soviet Union who had done business with some of Russia’s richest and most notorious oligarchs. Together, their firms made Trump an offer he couldn’t refuse: The developers would finance and build Trump SoHo themselves. In return for lending his name to the project, Trump would get 18 percent of the profits—without putting up any of his own money.
One of the developers, Tamir Sapir, had followed an unlikely path to riches. After emigrating from the Soviet Union in the 1970s, he had started out driving a cab in New York City and ended up a billionaire living in Trump Tower. His big break came when he co-founded a company that sold high-tech electronics. According to the FBI, Sapir’s partner in the firm was a “member or associate” of Ivankov’s mob in Brighton Beach. No charges were ever filed, and Sapir denied having any mob ties. “It didn’t happen,” he told The New York Times. “Everything was done in the most legitimate way.”
Trump, who described Sapir as a “great friend,” bought 200 televisions from his electronics company. In 2007, he hosted the wedding of Sapir’s daughter at Mar-a-Lago, and later attended her infant son’s bris.
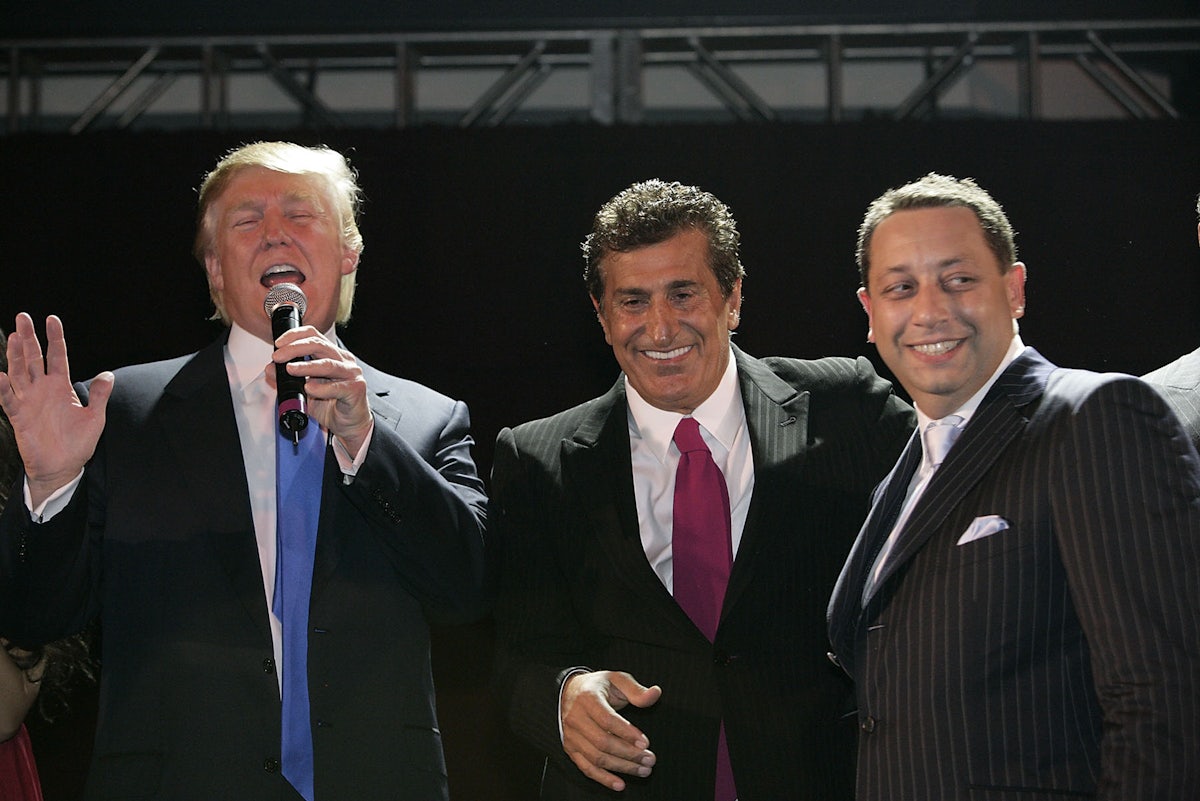

In 2007, Trump celebrated the launch of Trump SoHo with partners Tevfik Arif (center) and Felix Sater (right). Arif was later acquitted on charges of running a prostitution ring. Mark Von Holden/WireImage/Getty
Sapir also introduced Trump to Tevfik Arif, his partner in the Trump SoHo deal. On paper, at least, Arif was another heartwarming immigrant success story. He had graduated from the Moscow Institute of Trade and Economics and worked as a Soviet trade and commerce official for 17 years before moving to New York and founding Bayrock. Practically overnight, Arif became a wildly successful developer in Brooklyn. In 2002, after meeting Trump, he moved Bayrock’s offices to Trump Tower, where he and his staff of Russian émigrés set up shop on the twenty-fourth floor.
Trump worked closely with Bayrock on real estate ventures in Russia, Ukraine, and Poland. “Bayrock knew the investors,” he later testified. Arif “brought the people up from Moscow to meet with me.” He boasted about the deal he was getting: Arif was offering him a 20 to 25 percent cut on his overseas projects, he said, not to mention management fees. “It was almost like mass production of a car,” Trump testified.
But Bayrock and its deals quickly became mired in controversy. Forbes and other publications reported that the company was financed by a notoriously corrupt group of oligarchs known as The Trio. In 2010, Arif was arrested by Turkish prosecutors and charged with setting up a prostitution ring after he was found aboard a boat—chartered by one of The Trio—with nine young women, two of whom were 16 years old. The women reportedly refused to talk, and Arif was acquitted. According to a lawsuit filed that same year by two former Bayrock executives, Arif started the firm “backed by oligarchs and money they stole from the Russian people.” In addition, the suit alleges, Bayrock “was substantially and covertly mob-owned and operated.” The company’s real purpose, the executives claim, was to develop hugely expensive properties bearing the Trump brand—and then use the projects to launder money and evade taxes.
The lawsuit, which is ongoing, does not claim that Trump was complicit in the alleged scam. Bayrock dismissed the allegations as “legal conclusions to which no response is required.” But last year, after examining title deeds, bank records, and court documents, the Financial Times concluded that Trump SoHo had “multiple ties to an alleged international money-laundering network.” In one case, the paper reported, a former Kazakh energy minister is being sued in federal court for conspiring to “systematically loot hundreds of millions of dollars of public assets” and then purchasing three condos in Trump SoHo to launder his “ill-gotten funds.”

During his collaboration with Bayrock, Trump also became close to the man who ran the firm’s daily operations—a twice-convicted felon with family ties to Semion Mogilevich. In 1974, when he was eight years old, Felix Sater and his family emigrated from Moscow to Brighton Beach. According to the FBI, his father—who was convicted for extorting local restaurants, grocery stores, and a medical clinic—was a Mogilevich boss. Sater tried making it as a stockbroker, but his career came to an abrupt end in 1991, after he stabbed a Wall Street foe in the face with a broken margarita glass during a bar fight, opening wounds that required 110 stitches. (Years later, in a deposition, Trump downplayed the incident, insisting that Sater “got into a barroom fight, which a lot of people do.”) Sater lost his trading license over the attack, and served a year in prison.
In 1998, Sater pleaded guilty to racketeering—operating a “pump and dump” stock fraud in partnership with alleged Russian mobsters that bilked investors of at least $40 million. To avoid prison time, Sater turned informer. But according to the lawsuit against Bayrock, he also resumed “his old tricks.” By 2003, the suit alleges, Sater controlled the majority of Bayrock’s shares—and proceeded to use the firm to launder hundreds of millions of dollars, while skimming and extorting millions more. The suit also claims that Sater committed fraud by concealing his racketeering conviction from banks that invested hundreds of millions in Bayrock, and that he threatened “to kill anyone at the firm he thought knew of the crimes committed there and might report it.” In court, Bayrock has denied the allegations, which Sater’s attorney characterizes as “false, fabricated, and pure garbage.”
By Sater’s account, in sworn testimony, he was very tight with Trump. He flew to Colorado with him, accompanied Donald Jr. and Ivanka on a trip to Moscow at Trump’s invitation, and met with Trump’s inner circle “constantly.” In Trump Tower, he often dropped by Trump’s office to pitch business ideas—“just me and him.”
Trump seems unable to recall any of this. “Felix Sater, boy, I have to even think about it,” he told the Associated Press in 2015. Two years earlier, testifying in a video deposition, Trump took the same line. If Sater “were sitting in the room right now,” he swore under oath, “I really wouldn’t know what he looked like.” He added: “I don’t know him very well, but I don’t think he was connected to the mafia.”
Trump and his lawyers say that he was unaware of Sater’s criminal past when he signed on to do business with Bayrock. That’s plausible, since Sater’s plea deal in the stock fraud was kept secret because of his role as an informant. But even after The New York Times revealed Sater’s criminal record in 2007, he continued to use office space provided by the Trump Organization. In 2010, he was even given an official Trump Organization business card that read: FELIX H. SATER, SENIOR ADVISOR TO DONALD TRUMP.
In 2013, police burst into Unit 63A of Trump Tower and rounded up 29 suspects in a $100 million money-laundering scheme.
Sater apparently remains close to Trump’s inner circle. Earlier this year, one week before National Security Advisor Michael Flynn was fired for failing to report meetings with Russian officials, Trump’s personal attorney reportedly hand-delivered to Flynn’s office a “back-channel plan” for lifting sanctions on Russia. The co-author of the plan, according to the Times: Felix Sater.
In the end, Trump’s deals with Bayrock, like so much of his business empire, proved to be more glitter than gold. The international projects in Russia and Poland never materialized. A Trump tower being built in Fort Lauderdale ran out of money before it was completed, leaving behind a massive concrete shell. Trump SoHo ultimately had to be foreclosed and resold. But his Russian investors had left Trump with a high-profile property he could leverage. The new owners contracted with Trump to run the tower; as of April, the president and his daughter Ivanka were still listed as managers of the property. In 2015, according to the federal financial disclosure reports, Trump made $3 million from Trump SoHo.
In April 2013, a little more than two years before Trump rode the escalator to the ground floor of Trump Tower to kick off his presidential campaign, police burst into Unit 63A of the high-rise and rounded up 29 suspects in two gambling rings. The operation, which prosecutors called “the world’s largest sports book,” was run out of condos in Trump Tower—including the entire fifty-first floor of the building. In addition, unit 63A—a condo directly below one owned by Trump—served as the headquarters for a “sophisticated money-laundering scheme” that moved an estimated $100 million out of the former Soviet Union, through shell companies in Cyprus, and into investments in the United States. The entire operation, prosecutors say, was working under the protection of Alimzhan Tokhtakhounov, whom the FBI identified as a top Russian vor closely allied with Semion Mogilevich. In a single two-month stretch, according to the federal indictment, the money launderers paid Tokhtakhounov $10 million.
Tokhtakhounov, who had been indicted a decade earlier for conspiring to fix the ice-skating competition at the 2002 Winter Olympics, was the only suspect to elude arrest. For the next seven months, the Russian crime boss fell off the radar of Interpol, which had issued a red alert. Then, in November 2013, he suddenly appeared live on international television—sitting in the audience at the Miss Universe pageant in Moscow. Tokhtakhounov was in the VIP section, just a few seats away from the pageant owner, Donald Trump.
After the pageant, Trump bragged about all the powerful Russians who had turned out that night, just to see him. “Almost all of the oligarchs were in the room,” he told Real Estate Weekly. Contacted by Mother Jones, Tokhtakhounov insisted that he had bought his own ticket and was not a VIP. He also denied being a mobster, telling The New York Times that he had been indicted in the gambling ring because FBI agents “misinterpreted his Russian slang” on their Trump Tower wiretaps, when he was merely placing $20,000 bets on soccer games.
Both the White House and the Trump Organization declined to respond to questions for this story. On the few occasions he has been questioned about his business entanglements with Russians, however, Trump has offered broad denials. “I tweeted out that I have no dealings with Russia,” he said at a press conference in January, when asked if Russia has any “leverage” over him, financial or otherwise. “I have no deals that could happen in Russia, because we’ve stayed away. And I have no loans with Russia. I have no loans with Russia at all.” In May, when he was interviewed by NBC’s Lester Holt, Trump seemed hard-pressed to think of a single connection he had with Russia. “I have had dealings over the years where I sold a house to a very wealthy Russian many years ago,” he said. “I had the Miss Universe pageant—which I owned for quite a while—I had it in Moscow a long time ago. But other than that, I have nothing to do with Russia.”
But even if Trump has no memory of the many deals that he and his business made with Russian investors, he certainly did not “stay away” from Russia. For decades, he and his organization have aggressively promoted his business there, seeking to entice investors and buyers for some of his most high-profile developments. Whether Trump knew it or not, Russian mobsters and corrupt oligarchs used his properties not only to launder vast sums of money from extortion, drugs, gambling, and racketeering, but even as a base of operations for their criminal activities. In the process, they propped up Trump’s business and enabled him to reinvent his image. Without the Russian mafia, it is fair to say, Donald Trump would not be president of the United States.
Semion Mogilevich, the Russian mob’s “boss of bosses,” also declined to respond to questions from the New Republic. “My ideas are not important to anybody,” Mogilevich said in a statement provided by his attorney. “Whatever I know, I am a private person.” Mogilevich, the attorney added, “has nothing to do with President Trump. He doesn’t believe that anybody associated with him lives in Trump Tower. He has no ties to America or American citizens.”
Back in 1999, the year before Trump staged his first run for president, Mogilevich gave a rare interview to the BBC. Living up to his reputation for cleverness, the mafia boss mostly joked and double-spoke his way around his criminal activities. (Q: “Why did you set up companies in the Channel Islands?” A: “The problem was that I didn’t know any other islands. When they taught us geography at school, I was sick that day.”) But when the exasperated interviewer asked, “Do you believe there is any Russian organized crime?” the “brainy don” turned half-serious.
“How can you say that there is a Russian mafia in America?” he demanded. “The word mafia, as far as I understand the word, means a criminal group that is connected with the political organs, the police and the administration. I don’t know of a single Russian in the U.S. Senate, a single Russian in the U.S. Congress, a single Russian in the U.S. government. Where are the connections with the Russians? How can there be a Russian mafia in America? Where are their connections?”
Two decades later, we finally have an answer to Mogilevich’s question.
Craig Unger is a contributing editor at Vanity Fair and the author of several books, including House of Bush, House of Saud.
