Politico
Hurricane Ian traumatized Floridians. It also erased their nest eggs.
Zack Colman and Katy O’Donnell – October 10, 2022

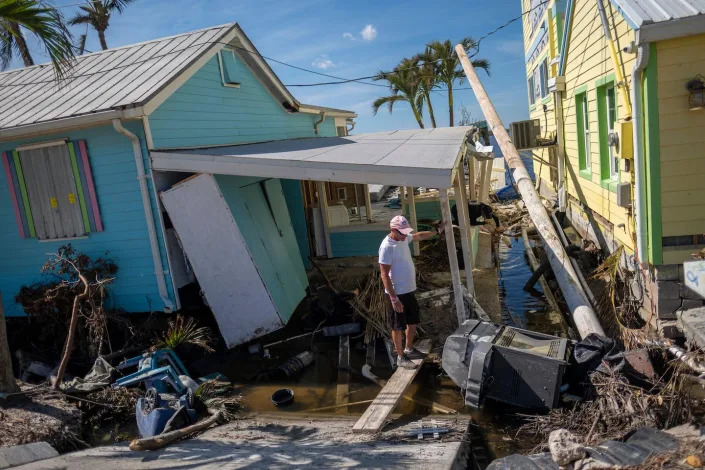
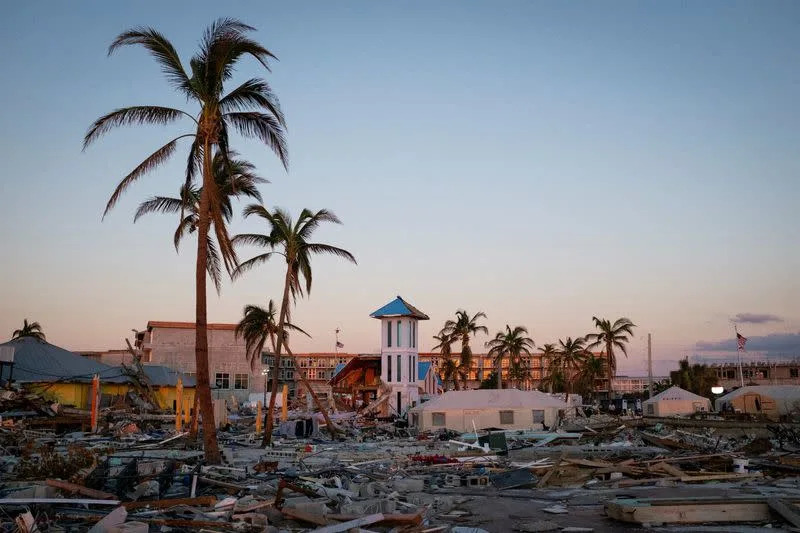
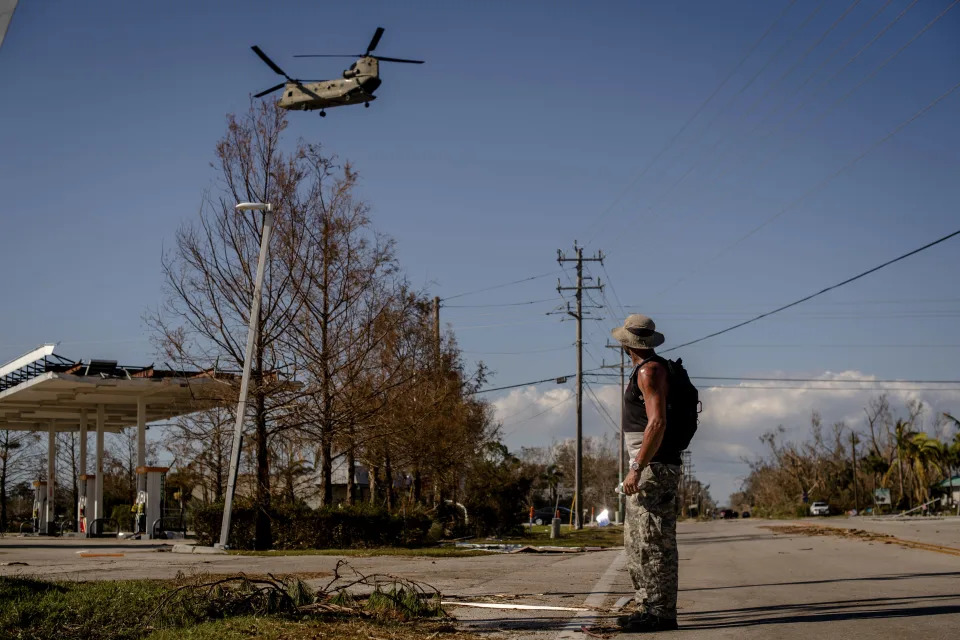
Hurricane Ian has displaced thousands of Floridians’ whose homes are now uninhabitable. The storm took their safety nets with it, too.
As Florida tallies the immediate tab from its deadliest hurricane in decades, the destruction it wreaked on homes will erase retirees’ nest eggs and families’ primary way of passing along wealth to new generations. That exposed the dangers of American dependence on housing as most people’s financial backstop and lifeline.
“The impacts of Hurricane Ian have stretched far and wide, especially to Southwest Florida seniors who’ve invested most of their livelihoods in properties across my district,” Rep. Byron Donalds (R-Fla.), who represents Lee County, said in an emailed statement. “In addition to the tremendous economic pressures induced by soaring inflation, this storm contributes additional pain to many on fixed incomes.”
As climate change makes natural disasters more frequent and severe — and threatens the viability of living in much of the country — Ian offered new evidence that Americans’ retirement funds and assets are in jeopardy in vulnerable areas.
“This is an enormous wealth shock,” said Benjamin Keys, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School of Business, who has researched the effects of climate-driven sea-level rise on Florida’s housing market.
It’s a problem with no easy policy solutions.
The Federal Housing Finance Agency, which regulates the government-controlled companies behind about half of the $12 trillion residential mortgage market, has begun assessing the risks that climate change poses to the mortgage and housing market. But it has historically allowed the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s flood insurance program to take the lead in protecting borrowers against flood damage — though independent analyses show that FEMA’s flood maps underestimate how many homes face flood danger.
Home ownership is the primary way most Americans build wealth. For decades, federal policy has placed a priority on making more Americans homeowners, seeing it as the clearest way to achieve long-lasting financial security and generational prosperity. But climate change is jeopardizing all that.
The risks Ian revealed are most pressing for retirees. People over 65 years old make up 29 percent of the population in Lee County, Fla. — ground zero for Ian damage — according to Census data. Among midsize cities, business research firm AdvisorSmith foundthat the Lee County communities of Cape Coral and Fort Myers experienced the sixth- and seventh-greatest increases nationally in the numbers of people older than 65 years in 2019. Those populations have grown even more since the beginning of the coronavirus pandemic.
Many of the Fort Myers and Cape Coral neighborhoods that Ian battered are middle-income, blue-collar areas, not at all like the multimillion-dollar mansions just down the coast in Naples, said Dave Stevens, a former CEO of the Mortgage Bankers Association and Federal Housing Administration commissioner. They’re also hotbeds for retirees who had “their life savings wrapped up in real estate” and now live on a fixed income, he added.
“It’s an important asset — obviously not one that’s replaceable, unless you’re part of the wealthy class,” said Stevens, who is now CEO of consulting firm Mountain Lake Consulting.
Retirees whose homes were destroyed also lost an important part of their wealth planning, said Jesse Keenan, professor of sustainable real estate at Tulane University’s School of Architecture. The market for reverse mortgages, which allow a person with a fully paid-off home to borrow against the house in exchange for cash, is “very strong” in Cape Coral, he said. But without that real estate asset, there’s no way to tap into that equity for everyday living.
If these people already had a reverse mortgage, they’re likely using those funds to make repairs now — especially if they were uninsured, Keenan added.
Climate science studies have shown that warmer temperatures are causing hurricanes to accelerate and grow stronger whenever they do form. Early analyses of Ian showed that human-driven climate change probably made the hurricane drop 10 percent more rainfall compared with a world without warming. That tracks with other recent hurricanes such as Harvey in 2017, which devastated the Houston area with more than 51 inches of rain when it stalled over the city for three days.
Climate and natural disaster risk-modeling firm RMS estimated that Ian inflicted between $53 billion and $74 billion in private market insured losses, with a best estimate of $67 billion. That would make Ian the second-costliest hurricane in U.S. history, slotting behind Hurricane Katrina’s nearly $90 billion in insured losses in 2021 dollars, according to the Insurance Information Institute.
Ian will result in anywhere from $30 billion to $42 billion of insured damage from wind alone, without accounting for flooding damage, according to an estimate from CoreLogic, a property data and analytics company.
Homes with federally backed mortgages in the 100-year floodplain are required to carry flood insurance, but that covers only up to $250,000. In contrast, the average mortgage borrower in the area covering Cape Coral and Fort Myers has $316,499 of equity in their homes, according to CoreLogic.
Boosting flood insurance would buttress homeowners against severe losses. But many homeowners fail to keep current with legal requirements to purchase that protection — a subject that’s been part of congressional inquiries and Government Accountability Office reports. And FEMA, despite administering the federal flood insurance program, maintains it does not have the ability to enforce those requirements.
Homes that are fully paid off don’t require flood insurance, with many choosing to forgo it. And even homes outside the 100-year floodplain, where this insurance is not required, incur flood damage. In Lee County, federal flood insurance uptake was far higher than the national average, but still reached only 30 percent of households, according to FEMA data.
“Issues related to flood insurance are convoluted and frustrating, and Hurricane Ian has brought these matters to the forefront, which the State will likely address soon,” Donalds said in his emailed statement.
Even people who have insurance must spend up to their deductibles before their claims are covered, which can be difficult for retirees on fixed incomes.
“For retirees it’s a double whammy, because many fixed-income retirees buy their homes with cash, and even if they’re in the flood zone they don’t have coverage because the [National Flood Insurance Program] enforces through mortgages,” said Tom Larsen, associate vice president for hazard and risk management at CoreLogic.
“Flood damage can go from zero to a very high number very rapidly,” he said.
Fort Myers is far from the only place where personal safety nets and inheritances are under siege.
Rising temperatures in cities such as Orlando and Phoenix could start to lower the value of real estate and the ability of Americans to depend on their homes as a safety net.
Investment research firm RisQ, real estate company Climate Core Capital and the Harvard Graduate School of Design explored how quickly some of the nation’s most desirable real estate markets would heat up beyond the point of tolerable human living in what they called a “Death Valley Index.” They measured how soon certain areas’ climates would mimic the historical climate of Death Valley, the site of the hottest-ever temperature on record, where between 1981 and 2010 daily temperatures hit 95 degrees Fahrenheit across 161 days on average every year.
The exercise concluded that Miami and Houston will achieve that mark by 2026 when high temperatures and humidity are taken into account. Austin would reach it by 2027, Tampa by 2029 and Phoenix by 2038. Orlando already has.
That climate would bring health risks from being outdoors even for a few hours, raising questions of how desirable those locations will be in the future, said Owen Woolcock, a partner at Climate Core Capital. People who purchased homes in those areas — many of which are retiree havens — could be left with properties worth less than what they were purchased for, Woolcock said.
“People need to think about climate change as a wealth destruction event,” he said. “It is going to make these enormous incisions in net worth at the household level and in the regional or local economy level.”