The Oak Ridger
How hot is too hot for humans? Local physician tells how climate change affects us
Carolyn Krause – October 6, 2023
As the Earth heats up owing to increased fossil fuel use and deforestation, Americans should be aware that heat waves are the leading cause of weather-related deaths in the country and that certain high temperature ranges can endanger our health and even the ability of our cellphones to work.
That was the message presented by Elaine Bunick, a retired endocrinologist who has traveled to Ghana, Haiti and other countries on medical mission trips. In her recent talk to Altrusa International of Oak Ridge, she presented extensive information on the effects of climate change on the environment, human health and healthcare facilities.
She provided advice on how to protect yourself from excessive heat. And she relayed predictions on impending health care worker shortages that likely made some audience members hot and bothered.
This summer in Oak Ridge, she said, residents experienced 33 days with temperatures greater than 90 degrees Fahrenheit. July was the hottest month. Bunick said people can expect to have to endure 20 to 30 more days a year of sizzling heat with peak temperatures over 90.
A check with Methodist Medical Center of Oak Ridge indicated that the emergency room reported more cardiac issues and interventions this year than in the past, but an increased death rate was not observed. Heat waves and air pollution from burning forests can cause heart problems.
Heat is greater risk for some
Bunick said people with chronic medical conditions, such as heart disease, respiratory disorders, diabetes, obesity and kidney ailments, have a greater risk for succumbing to heat illnesses.
“Medications such as antidepressants, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, antipsychotics and opioids alter your ability to handle the heat,” she added.
The increased heat, she said, will especially endanger the health of outdoor workers, such as farmers, police officers, firefighters, road workers, power line maintenance workers and transporters of supplies to stores and homes. The loss of labor hours, she added, will hurt the economy.
Others who are most susceptible to falling ill from excessive heat are persons older than 65, infants, children, pregnant women, people with pre-existing medical conditions and disabilities, athletes and people living in lower-income households or those who are homeless.
Take care of each other
“We have to be adaptable and protect each other to survive,” Bunick said. She cited statistics on the future of health care in the nation.
“The U.S. is predicted to have a shortage of 129,000 doctors and 200,000 nurse practitioners, physician assistants and technical personnel by 2034,” she said. “That’s scary. Our population has an increasing number of seniors – we’re almost 25% of the population. Who is going to care for us? We’re going to have to care for each other.”

She noted that “in the early 2000s, the U.S. government put a cap on the number of doctors, nurses and physician assistants that can be trained. To this day they have not rescinded that order, so we have a growing shortage of trained medical staff. It takes 15 years to train a specialist like me and six years to train a nurse.”
The average temperature of the earth’s surface has been around 58 degrees Fahrenheit. This year, Bunick said, “the earth’s average surface temperature rose to 62.9 degrees and the oceans reached a peak of 69 degrees, almost the temperature of bath water. That was hottest ocean temperature ever recorded.”
Heat indexes, heat exhaustion and more
So, how hot is too hot? What are the dangerous temperatures and heat indexes for humans?
A normal adult body temperature, when taken orally, can range from 97.6 to 99.6 degrees Fahrenheit. According to Bunick, “The hottest air temperature for human survival is 123.8 degrees; beyond that you’re unlikely to survive. A body temperature over 108.14 degrees causes the body to become scrambled because the heat fries the proteins, denaturing them and causing dysfunction of enzymes and harm to the brain. Death can occur within six hours. Building heat tolerance and acclimatization takes about six weeks.”
According to one of her slides, a human body temperature of 103 to 104 degrees Fahrenheit can cause confusion and impaired judgment, and a temperature of 109 to 110 degrees Fahrenheit can cause brain damage, seizures, cardio-respiratory collapse, shock and death. The highest temperature recorded of a person surviving a heat stroke was 115.7 degrees Fahrenheit.
The heat index is a measure of the interaction of temperature and humidity. “Sweat cools the body by evaporation but if it’s too humid, you can’t add any more moisture to the air,” she said. A heat index of 95 degrees is considered the absolute limit of human tolerance above which the body cannot lose heat efficiently enough to maintain core temperature and avoid brain and organ damage within about six hours.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke are headache, nausea, dizziness, weakness, irritability, thirst, heavy sweating, elevated body temperature, confusion, altered mental status, slurred speech, loss of consciousness, profuse sweating, and seizures. Under these conditions, the body temperature is higher than 104 degrees Fahrenheit.
To protect yourself from heat exhaustion or heat stroke when you’re outdoors on hot days, the CDC recommends that you wear lightweight, light-colored, loose-fitting clothing and a sun hat; take breaks to drink water and cool down in an air-conditioned or shady place; wear sunscreen and sunglasses when you’re outside; drink Gatorade or other drinks with electrolytes; avoid alcoholic beverages, splash yourself with water or use a cold, wet cloth to cool down and check your body temperature periodically.
To treat someone with heat exhaustion, move them to a cool area, give frequent sips of cool water, apply cold and wet compresses, remove unnecessary clothing, call 911 or take the individual to the ER for medical evaluation and treatment. If you and others are on a hike on a hot day, she warned, be sure you keep your cellphone cool and out of direct sunlight or a hot car (120 degrees). Between 96 and 109 degrees the battery will be so damaged that your phone will no longer allow you to make emergency calls.
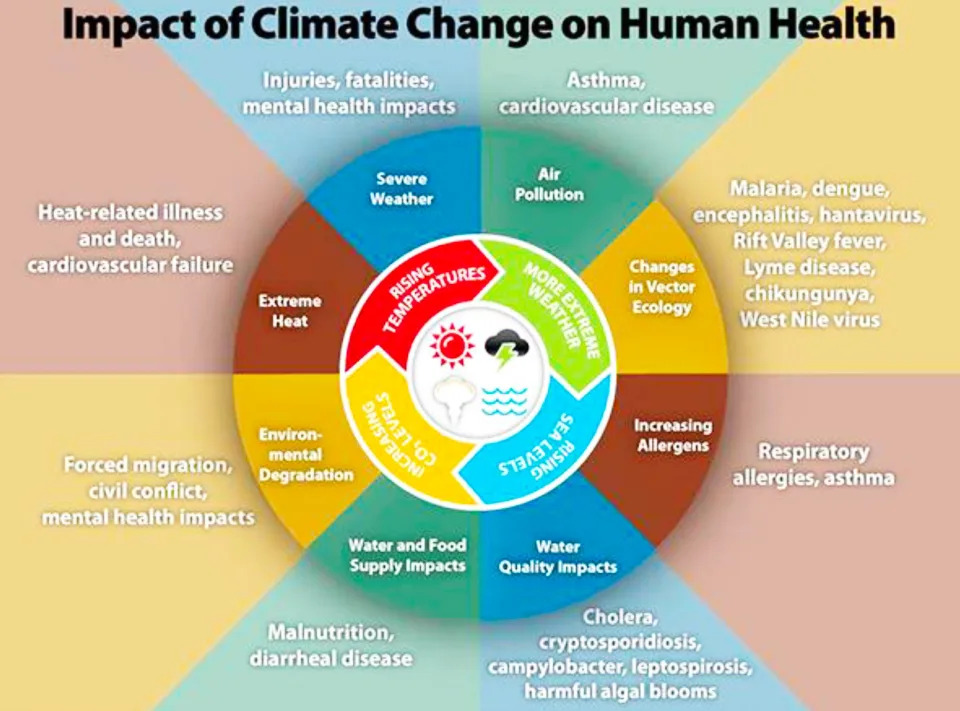
Bunick noted that weather-related and climate-related events can threaten human health and safety in other ways. Wildfires and house fires can release cancer-causing and other irritating particles to the air, causing respiratory disease and heart issues. She advised checking on the EPA Air Quality Index (stay inside when the air is labeled Code Orange, Red, Purple or Maroon) and wearing N95 or KN95 masks if you must be outside when the air is unhealthy.
Wear insect repellant because ticks and mosquitoes migrating north as the climate warms carry Lyme disease, West Nile virus, dengue fever and malaria, according to one of her slides. Climate change can increase the probability that people get sick from disease-carrying organisms entering drinking water and from harmful algal blooms caused by algae and bacteria present in waters where people swim, causing eye irritation and respiratory illness especially in people with asthma.
“In 2022 the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration announced there were 18 weather-related disasters costing over $1 billion each,” Bunick said.
Some of these disasters caused flooding, leading to drownings and homes destroyed by unhealthy mold. The disasters included heat waves, drought, flooding, hailstorms, hurricanes, tornadoes and winter storms. The death and destruction from these disasters cause mental health problems in victims.
Hospitals are preparing
Bunick said that administrators of hospitals, which use lots of electricity and produce 10% of U.S. greenhouse gases, as well as their healthcare workforce, are preparing for climate-related emergencies and extreme weather events that can disrupt operations, including hurricanes, floods and wildfires. Medicines in hospital pharmacies may be damaged by floods or by the heat, causing them to lose their potency. She gave an example close to home.
“Many hospitals keep their computers, medicines and other important supplies in the basement,” she said. “Recently, there was a water main break at Fort Sanders hospital in Knoxville. My son-in-law, who’s in charge of home infusion therapy at Fort Sanders, had to rush to save the medication in the hospital basement pharmacy from six inches of water!”
