The Nation
Noam Chomsky Diagnoses the Trump Era
The president has abetted the collapse of a decaying system; Chomsky explains how.
By Noam Chomsky and David Barsamian October 4, 2017
 Noam Chomsky addresses the audience at the National Autonomous University’s Educational Investigation Institute in Mexico City. (Reuters / Jorge Dan)
Noam Chomsky addresses the audience at the National Autonomous University’s Educational Investigation Institute in Mexico City. (Reuters / Jorge Dan)
This article originally appeared at TomDispatch.com.
This interview has been excerpted from Global Discontents: Conversations on the Rising Threats to Democracy, the new book by Noam Chomsky and David Barsamian to be published this December.
David Barsamian: You have spoken about the difference between Trump’s buffoonery, which gets endlessly covered by the media, and the actual policies he is striving to enact, which receive less attention. Do you think he has any coherent economic, political, or international policy goals? What has Trump actually managed to accomplish in his first months in office?
Noam Chomsky: There is a diversionary process under way, perhaps just a natural result of the propensities of the figure at center stage and those doing the work behind the curtains.
At one level, Trump’s antics ensure that attention is focused on him, and it makes little difference how. Who even remembers the charge that millions of illegal immigrants voted for Clinton, depriving the pathetic little man of his Grand Victory? Or the accusation that Obama had wiretapped Trump Tower? The claims themselves don’t really matter. It’s enough that attention is diverted from what is happening in the background. There, out of the spotlight, the most savage fringe of the Republican Party is carefully advancing policies designed to enrich their true constituency: the Constituency of private power and wealth, “the masters of mankind,” to borrow Adam Smith’s phrase.
These policies will harm the irrelevant general population and devastate future generations, but that’s of little concern to the Republicans. They’ve been trying to push through similarly destructive legislation for years. Paul Ryan, for example, has long been advertising his ideal of virtually eliminating the federal government, apart from service to the Constituency—though in the past he’s wrapped his proposals in spreadsheets so they would look wonkish to commentators. Now, while attention is focused on Trump’s latest mad doings, the Ryan gang and the executive branch are ramming through legislation and orders that undermine workers’ rights, cripple consumer protections, and severely harm rural communities. They seek to devastate health programs, revoking the taxes that pay for them in order to further enrich their constituency, and to eviscerate the Dodd-Frank Act, which imposed some much-needed constraints on the predatory financial system that grew during the neoliberal period.
That’s just a sample of how the wrecking ball is being wielded by the newly empowered Republican Party. Indeed, it is no longer a political party in the traditional sense. Conservative political analysts Thomas Mann and Norman Ornstein have described it more accurately as a “radical insurgency,” one that has abandoned normal parliamentary politics.
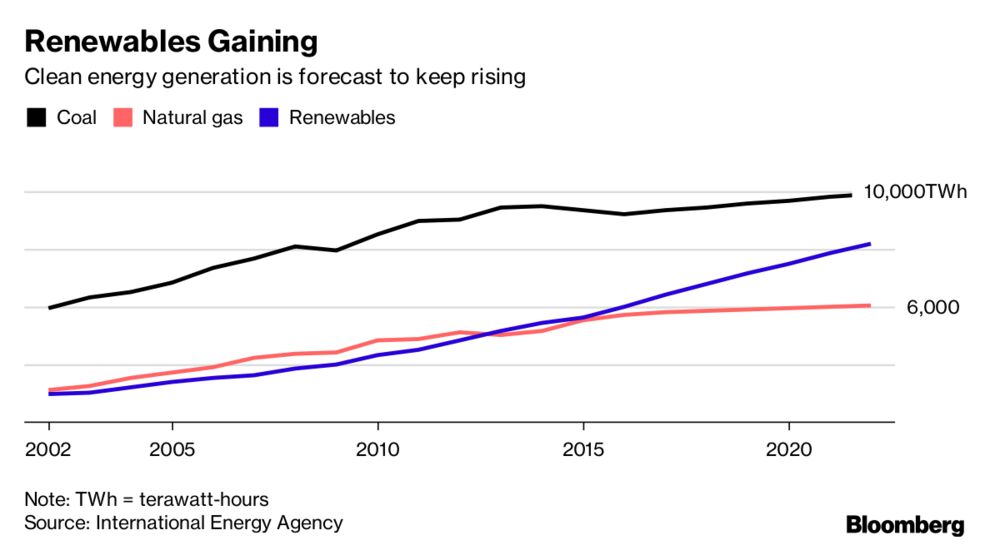
Much of this is being carried out stealthily, in closed sessions, with as little public notice as possible. Other Republican policies are more open, such as pulling out of the Paris climate agreement, thereby isolating the US as a pariah state that refuses to participate in international efforts to confront looming environmental disaster. Even worse, they are intent on maximizing the use of fossil fuels, including the most dangerous; dismantling regulations; and sharply cutting back on research and development of alternative energy sources, which will soon be necessary for decent survival.
The reasons behind the policies are a mix. Some are simply service to the Constituency. Others are of little concern to the “masters of mankind” but are designed to hold on to segments of the voting bloc that the Republicans have cobbled together, since Republican policies have shifted so far to the right that their actual proposals would not attract voters. For example, terminating support for family planning is not service to the Constituency. Indeed, that group may mostly support family planning. But terminating that support appeals to the evangelical Christian base—voters who close their eyes to the fact that they are effectively advocating more unwanted pregnancies and, therefore, increasing the frequency of resort to abortion, under harmful and even lethal conditions.
Not all of the damage can be blamed on the con man who is nominally in charge, on his outlandish appointments, or on the congressional forces he has unleashed. Some of the most dangerous developments under Trump trace back to Obama initiatives—initiatives passed, to be sure, under pressure from the Republican Congress.
The most dangerous of these has barely been reported. A very important study in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, published in March 2017, reveals that the Obama nuclear-weapons-modernization program has increased “the overall killing power of existing US ballistic missile forces by a factor of roughly three—and it creates exactly what one would expect to see, if a nuclear-armed state were planning to have the capacity to fight and win a nuclear war by disarming enemies with a surprise first strike.” As the analysts point out, this new capacity undermines the strategic stability on which human survival depends. And the chilling record of near disaster and reckless behavior of leaders in past years only shows how fragile our survival is. Now this program is being carried forward under Trump. These developments, along with the threat of environmental disaster, cast a dark shadow over everything else—and are barely discussed, while attention is claimed by the performances of the showman at center stage.
Whether Trump has any idea what he and his henchmen are up to is not clear. Perhaps he is completely authentic: an ignorant, thin-skinned megalomaniac whose only ideology is himself. But what is happening under the rule of the extremist wing of the Republican organization is all too plain.
DB: Do you see any encouraging activity on the Democrats’ side? Or is it time to begin thinking about a third party?
NC: There is a lot to think about. The most remarkable feature of the 2016 election was the Bernie Sanders campaign, which broke the pattern set by over a century of US political history. A substantial body of political science research convincingly establishes that elections are pretty much bought; campaign funding alone is a remarkably good predictor of electability, for Congress as well as for the presidency. It also predicts the decisions of elected officials. Correspondingly, a considerable majority of the electorate—those lower on the income scale—are effectively disenfranchised, in that their representatives disregard their preferences. In this light, there is little surprise in the victory of a billionaire TV star with substantial media backing: direct backing from the leading cable channel, Rupert Murdoch’s Fox, and from highly influential right-wing talk radio; indirect but lavish backing from the rest of the major media, which was entranced by Trump’s antics and the advertising revenue that poured in.
The Sanders campaign, on the other hand, broke sharply from the prevailing model. Sanders was barely known. He had virtually no support from the main funding sources, was ignored or derided by the media, and labeled himself with the scare word “socialist.” Yet he is now the most popular political figure in the country by a large margin.
At the very least, the success of the Sanders campaign shows that many options can be pursued even within the stultifying two-party framework, with all of the institutional barriers to breaking free of it. During the Obama years, the Democratic Party disintegrated at the local and state levels. The party had largely abandoned the working class years earlier, even more so with Clinton trade and fiscal policies that undermined US manufacturing and the fairly stable employment it provided.
There is no dearth of progressive policy proposals. The program developed by Robert Pollin in his book Greening the Global Economy is one very promising approach. Gar Alperovitz’s work on building an authentic democracy based on worker self-management is another. Practical implementations of these approaches and related ideas are taking shape in many different ways. Popular organizations, some of them outgrowths of the Sanders campaign, are actively engaged in taking advantage of the many opportunities that are available.
At the same time, the established two-party framework, though venerable, is by no means graven in stone. It’s no secret that in recent years, traditional political institutions have been declining in the industrial democracies, under the impact of what is called “populism.” That term is used rather loosely to refer to the wave of discontent, anger, and contempt for institutions that has accompanied the neoliberal assault of the past generation, which led to stagnation for the majority alongside a spectacular concentration of wealth in the hands of a few.
Functioning democracy erodes as a natural effect of the concentration of economic power, which translates at once to political power by familiar means, but also for deeper and more principled reasons. The doctrinal pretense is that the transfer of decision-making from the public sector to the “market” contributes to individual freedom, but the reality is different. The transfer is from public institutions, in which voters have some say, insofar as democracy is functioning, to private tyrannies—the corporations that dominate the economy—in which voters have no say at all. In Europe, there is an even more direct method of undermining the threat of democracy: placing crucial decisions in the hands of the unelected troika—the International Monetary Fund, the European Central Bank, and the European Commission—which heeds the northern banks and the creditor community, not the voting population.
These policies are dedicated to making sure that society no longer exists, Margaret Thatcher’s famous description of the world she perceived—or, more accurately, hoped to create: one where there is no society, only individuals. This was Thatcher’s unwitting paraphrase of Marx’s bitter condemnation of repression in France, which left society as a “sack of potatoes,” an amorphous mass that cannot function. In the contemporary case, the tyrant is not an autocratic ruler—in the West, at least—but concentrations of private power.
The collapse of centrist governing institutions has been evident in elections: in France in mid-2017 and in the United States a few months earlier, where the two candidates who mobilized popular forces were Sanders and Trump—though Trump wasted no time in demonstrating the fraudulence of his “populism” by quickly ensuring that the harshest elements of the old establishment would be firmly ensconced in power in the luxuriating “swamp.”
These processes might lead to a breakdown of the rigid American system of one-party business rule with two competing factions, with varying voting blocs over time. They might provide an opportunity for a genuine “people’s party” to emerge, a party where the voting bloc is the actual constituency, and the guiding values merit respect.
DB: Trump’s first foreign trip was to Saudi Arabia. What significance do you see in that, and what does it mean for broader Middle East policies? And what do you make of Trump’s animus toward Iran?
NC: Saudi Arabia is the kind of place where Trump feels right at home: a brutal dictatorship, miserably repressive (notoriously so for women’s rights, but in many other areas as well), the leading producer of oil (now being overtaken by the United States), and with plenty of money. The trip produced promises of massive weapons sales—greatly cheering the Constituency—and vague intimations of other Saudi gifts. One of the consequences was that Trump’s Saudi friends were given a green light to escalate their disgraceful atrocities in Yemen and to discipline Qatar, which has been a shade too independent of the Saudi masters. Iran is a factor there. Qatar shares a natural gas field with Iran and has commercial and cultural relations with it, frowned upon by the Saudis and their deeply reactionary associates.
Iran has long been regarded by US leaders, and by US media commentary, as extraordinarily dangerous, perhaps the most dangerous country on the planet. This goes back to well before Trump. In the doctrinal system, Iran is a dual menace: It is the leading supporter of terrorism, and its nuclear programs pose an existential threat to Israel, if not the whole world. It is so dangerous that Obama had to install an advanced air defense system near the Russian border to protect Europe from Iranian nuclear weapons—which don’t exist, and which, in any case, Iranian leaders would use only if possessed by a desire to be instantly incinerated in return.
That’s the doctrinal system. In the real world, Iranian support for terrorism translates to support for Hezbollah, whose major crime is that it is the sole deterrent to yet another destructive Israeli invasion of Lebanon, and for Hamas, which won a free election in the Gaza Strip—a crime that instantly elicited harsh sanctions and led the US government to prepare a military coup. Both organizations, it is true, can be charged with terrorist acts, though not anywhere near the amount of terrorism that stems from Saudi Arabia’s involvement in the formation and actions of jihadi networks.
As for Iran’s nuclear-weapons programs, US intelligence has confirmed what anyone can easily figure out for themselves: If they exist, they are part of Iran’s deterrent strategy. There is also the unmentionable fact that any concern about Iranian weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) could be alleviated by the simple means of heeding Iran’s call to establish a WMD-free zone in the Middle East. Such a zone is strongly supported by the Arab states and most of the rest of the world and is blocked primarily by the United States, which wishes to protect Israel’s WMD capabilities.
Since the doctrinal system falls apart on inspection, we are left with the task of finding the true reasons for US animus toward Iran. Possibilities readily come to mind. The United States and Israel cannot tolerate an independent force in a region that they take to be theirs by right. An Iran with a nuclear deterrent is unacceptable to rogue states that want to rampage however they wish throughout the Middle East. But there is more to it than that. Iran cannot be forgiven for overthrowing the dictator installed by Washington in a military coup in 1953, a coup that destroyed Iran’s parliamentary regime and its unconscionable belief that Iran might have some claim on its own natural resources. The world is too complex for any simple description, but this seems to me the core of the tale.
It also wouldn’t hurt to recall that in the past six decades, scarcely a day has passed when Washington was not tormenting Iranians. After the 1953 military coup came US support for a dictator described by Amnesty International as a leading violator of fundamental human rights. Immediately after his overthrow came the US-backed invasion of Iran by Saddam Hussein, no small matter. Hundreds of thousands of Iranians were killed, many by chemical weapons. Reagan’s support for his friend Saddam was so extreme that when Iraq attacked a US ship, the USS Stark, killing 37 American sailors, it received only a light tap on the wrist in response. Reagan also sought to blame Iran for Saddam’s horrendous chemical warfare attacks on Iraqi Kurds.
Eventually, the United States intervened directly in the Iran-Iraq War, leading to Iran’s bitter capitulation. Afterward, George H.W. Bush invited Iraqi nuclear engineers to the United States for advanced training in nuclear-weapons production—an extraordinary threat to Iran, quite apart from its other implications. And, of course, Washington has been the driving force behind harsh sanctions against Iran that continue to the present day.
Trump, for his part, has joined the harshest and most repressive dictators in shouting imprecations at Iran. As it happens, Iran held an election during his Middle East travel extravaganza—an election which, however flawed, would be unthinkable in the land of his Saudi hosts, who also happen to be the source of the radical Islamism that is poisoning the region. But US animus against Iran goes far beyond Trump himself. It includes those regarded as the “adults” in the Trump administration, like James “Mad Dog” Mattis, the secretary of defense. And it stretches a long way into the past.
DB: What are the strategic issues where Korea is concerned? Can anything be done to defuse the growing conflict?
NC: Korea has been a festering problem since the end of World War II, when the hopes of Koreans for unification of the peninsula were blocked by the intervention of the great powers, the United States bearing primary responsibility.
The North Korean dictatorship may well win the prize for brutality and repression, but it is seeking and to some extent carrying out economic development, despite the overwhelming burden of a huge military system. That system includes, of course, a growing arsenal of nuclear weapons and missiles, which pose a threat to the region and, in the longer term, to countries beyond—but its function is to be a deterrent, one that the North Korean regime is unlikely to abandon as long as it remains under threat of destruction.
Today, we are instructed that the great challenge faced by the world is how to compel North Korea to freeze these nuclear and missile programs. Perhaps we should resort to more sanctions, cyberwar, intimidation; to the deployment of the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) anti-missile system, which China regards as a serious threat to its own interests; perhaps even to direct attack on North Korea—which, it is understood, would elicit retaliation by massed artillery, devastating Seoul and much of South Korea even without the use of nuclear weapons.
But there is another option, one that seems to be ignored: We could simply accept North Korea’s offer to do what we are demanding. China and North Korea have already proposed that North Korea freeze its nuclear and missile programs. The proposal, though, was rejected at once by Washington, just as it had been two years earlier, because it includes a quid pro quo: It calls on the United States to halt its threatening military exercises on North Korea’s borders, including simulated nuclear-bombing attacks by B-52s.
The Chinese-North Korean proposal is hardly unreasonable. North Koreans remember well that their country was literally flattened by US bombing, and many may recall how US forces bombed major dams when there were no other targets left. There were gleeful reports in American military publications about the exciting spectacle of a huge flood of water wiping out the rice crops on which “the Asian” depends for survival. They are very much worth reading, a useful part of historical memory.
The offer to freeze North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs in return for an end to highly provocative actions on North Korea’s border could be the basis for more far-reaching negotiations, which could radically reduce the nuclear threat and perhaps even bring the North Korea crisis to an end. Contrary to much inflamed commentary, there are good reasons to think such negotiations might succeed. Yet even though the North Korean programs are constantly described as perhaps the greatest threat we face, the Chinese-North Korean proposal is unacceptable to Washington, and is rejected by US commentators with impressive unanimity. This is another entry in the shameful and depressing record of near-reflexive preference for force when peaceful options may well be available.
The 2017 South Korean elections may offer a ray of hope. Newly elected President Moon Jae-in seems intent on reversing the harsh confrontationist policies of his predecessor. He has called for exploring diplomatic options and taking steps toward reconciliation, which is surely an improvement over the angry fist-waving that might lead to real disaster.
DB: You have in the past expressed concern about the European Union. What do you think will happen as Europe becomes less tied to the US and the UK?
NC: The EU has fundamental problems, notably the single currency with no political union. It also has many positive features. There are some sensible ideas aimed at saving what is good and improving what is harmful. Yanis Varoufakis’s DiEM25 initiative for a democratic Europe is a promising approach.
The UK has often been a US surrogate in European politics. Brexit might encourage Europe to take a more independent role in world affairs, a course that might be accelerated by Trump policies that increasingly isolate us from the world. While he is shouting loudly and waving an enormous stick, China could take the lead on global energy policies while extending its influence to the west and, ultimately, to Europe, based on the Shanghai Cooperation Organization and the New Silk Road.
That Europe might become an independent “third force” has been a matter of concern to US planners since World War II. There have long been discussions of something like a Gaullist conception of Europe from the Atlantic to the Urals or, in more recent years, Gorbachev’s vision of a common Europe from Brussels to Vladivostok.
Whatever happens, Germany is sure to retain a dominant role in European affairs. It is rather startling to hear a conservative German chancellor, Angela Merkel, lecturing her US counterpart on human rights, and taking the lead, at least for a time, in confronting the refugee issue, Europe’s deep moral crisis. On the other hand, Germany’s insistence on austerity and paranoia about inflation and its policy of promoting exports by limiting domestic consumption have no slight responsibility for Europe’s economic distress, particularly the dire situation of the peripheral economies. In the best case, however, which is not beyond imagination, Germany could influence Europe to become a generally positive force in world affairs.
DB: What do you make of the conflict between the Trump administration and the US intelligence communities? Do you believe in the “deep state”?
NC: There is a national-security bureaucracy that has persisted since World War II. And national-security analysts, in and out of government, have been appalled by many of Trump’s wild forays. Their concerns are shared by the highly credible experts who set the Doomsday Clock, advanced to two and a half minutes to midnight as soon as Trump took office—the closest it has been to terminal disaster since 1953, when the US and USSR exploded thermonuclear weapons. But I see little sign that it goes beyond that, that there is any secret “deep state” conspiracy.
DB: To conclude, as we look forward to your 89th birthday, I wonder: Do you have a theory of longevity?
NC: Yes, it’s simple, really. If you’re riding a bicycle and you don’t want to fall off, you have to keep going—fast.
Noam Chomsky, Institute Professor emeritus at MIT, has written many books and articles on international affairs, in particular on Israel and Palestine. His latest book, Global Discontents: Conversations on the Rising Threats to Democracy, will be published in December 2017.
David Barsamian is the director of Alternative Radio in Boulder, Colorado (www.alternativeradio.org).
 © Getty Images
© Getty Images
 Image copyright SPL Image caption The world needs to be fed but in a more sustainable way, says the CiWF
Image copyright SPL Image caption The world needs to be fed but in a more sustainable way, says the CiWF Image copyright CiWF Image caption Future farming must work with Nature, not against it, says Philip Lymbery
Image copyright CiWF Image caption Future farming must work with Nature, not against it, says Philip Lymbery Interior Secretary Ryan Zinke testifies before the Senate Indian Affairs Committee on “Identifying Indian Affairs priorities for the Trump Administration” at the U.S. Capitol in Washington, U.S., March 8, 2017. REUTERS/Joshua Roberts
Interior Secretary Ryan Zinke testifies before the Senate Indian Affairs Committee on “Identifying Indian Affairs priorities for the Trump Administration” at the U.S. Capitol in Washington, U.S., March 8, 2017. REUTERS/Joshua Roberts Secretary of the Interior Ryan Zinke speaks during a daily press briefing at the White House in Washington, U.S.
Secretary of the Interior Ryan Zinke speaks during a daily press briefing at the White House in Washington, U.S. A colorized scanning electron micrograph image made available by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows the O157:H7 strain of the E. coli bacteria. (Photo: Janice Carr/CDC via AP)
A colorized scanning electron micrograph image made available by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows the O157:H7 strain of the E. coli bacteria. (Photo: Janice Carr/CDC via AP) Grass-fed, antibiotic- and growth-hormone-free cattle at Kookoolan Farm in Yamhill, Ore., on April 23, 2015. (Photo: Don Ryan/AP)
Grass-fed, antibiotic- and growth-hormone-free cattle at Kookoolan Farm in Yamhill, Ore., on April 23, 2015. (Photo: Don Ryan/AP) Noam Chomsky addresses the audience at the National Autonomous University’s Educational Investigation Institute in Mexico City. (Reuters / Jorge Dan)
Noam Chomsky addresses the audience at the National Autonomous University’s Educational Investigation Institute in Mexico City. (Reuters / Jorge Dan)
 Justin Hofman / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Justin Hofman / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Ashleigh Scully / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Ashleigh Scully / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Steve Winter / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Steve Winter / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Jack Dykinga / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Jack Dykinga / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Klaus Nigge / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Klaus Nigge / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Andrey Narchuk/Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Andrey Narchuk/Wildlife Photographer of the Year
 Laura Albiac Vilas / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Laura Albiac Vilas / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Tyohar Kastiel / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Tyohar Kastiel / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Qing Lin / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Qing Lin / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Laurent Ballesta / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Laurent Ballesta / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Sergey Gorshkov / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Sergey Gorshkov / Wildlife Photographer of the Year Mats Andersson / Wildlife Photographer of the Year
Mats Andersson / Wildlife Photographer of the Year

 Interior Secretary Ryan Zinke speaks March 29 at the Interior Department in Washington. (Molly Riley/AP)
Interior Secretary Ryan Zinke speaks March 29 at the Interior Department in Washington. (Molly Riley/AP)